0% found this document useful (0 votes)
112 views2 pagesOptical Fiber Systems Design
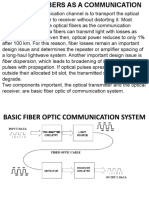
Optical transmitters and receivers are discussed. Key points include:
- Optical fibers can propagate light in different modes and configurations depending on factors like core and cladding indices and geometry.
- Optical transmitters like LEDs and laser diodes inject light into fibers via components like splices, connectors and couplers.
- Optical receivers like PIN photodiodes and APDs detect received light signals. Erbium-doped fiber amplifiers also discussed.
- Understanding fiber modes, transmitters, receivers and their application in modern fiber optic systems is covered. Characterization of microwave networks and components is also addressed.
Uploaded by
Shri shanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
112 views2 pagesOptical Fiber Systems Design
Optical transmitters and receivers are discussed. Key points include:
- Optical fibers can propagate light in different modes and configurations depending on factors like core and cladding indices and geometry.
- Optical transmitters like LEDs and laser diodes inject light into fibers via components like splices, connectors and couplers.
- Optical receivers like PIN photodiodes and APDs detect received light signals. Erbium-doped fiber amplifiers also discussed.
- Understanding fiber modes, transmitters, receivers and their application in modern fiber optic systems is covered. Characterization of microwave networks and components is also addressed.
Uploaded by
Shri shanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2