Practical No:1(A)
Aim: Draw Class diagram for ATM Machine.An automated teller machine(ATM)
or the automatic banking subsystem that provides bank customers with access to
financial transactions in a public space without the need for cashier,clerk or bank
teller.Customer uses bank ATM to check balances of his/her bank accounts,deposit
funds,withdraw cash and/or transfer funds which are the generalization alternative
of ATM transactions use case.
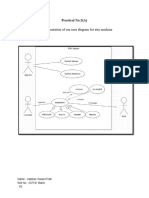
Diagram:
�Explanation:
1)Classes:
ATM: Represents the ATM machine itself. It will have methods to handle customer
transactions and communicate with the Bank class for processing.
● Attributes: location, atm number,managed by
● Methods: transactions(),identifies()
Bank: Represents the bank that manages customer accounts and transactions.
The ATM will communicate with this class to process the transactions.
● Methods: management(),maintenance()
● Customer: Represents a bank customer who uses the ATM.
● Attributes: name, accountNumber, pin
2)Relationships:
● The ATM class will have an association with the Bank class to communicate
with the bank for processing transactions.
● The ATM class will also have an association with the Customer class,
representing that customers interact with the ATM.
3)Inheritance:
● The specific types of transactions, such as Deposit, Withdrawal, and
Transfer, can be represented as subclasses of a Transaction class. This
Transaction class will be a generalization of these specific transaction types.
Here's a simplified textual representation of the inheritance relationship:
Transaction: Represents a general transaction that can be of different types
(Deposit, Withdrawal, Transfer).
● Methods: executeTransaction()
�
Deposit: Represents a deposit transaction. It will inherit from the Transaction
class and override the executeTransaction() method.
Withdrawal: Represents a withdrawal transaction. It will inherit from the
Transaction class and override the executeTransaction() method.
Transfer: Represents a funds transfer transaction. It will inherit from the
Transaction class and override the executeTransaction() method.
� Practical No:1(B)
Aim: Draw a class diagram for the scenario given below.This is an example that
models University Courses. Assume three classes' such as course, lecturer, student
and an interface person. Each course objects maintains a list of student on that
course and lecturer who has been assigned to teach that course. The course object
has behavior that allows adding and removing student to and from course,
assigning the teacher and getting a list of currently assigned student and currently
assigned teacher. A teacher may teach several courses but a course only has a
single teacher A lecturer object maintains a list of courses that it teaches, course is
attended by 0 or more student and student may attend multiple courses. A person
interface will have getName() and getEmailAddress() methods both lecturer and
student are shown to be the type of person.
�Explanation:
All Vehicles have some common attributes (speed and colour) and common
behaviour (turnLeft, turnRight) Bicycle and MotorVehicle are both kinds of
Vehicle and are therefore shown to inherit from Vehicle. To put this another way,
Vehicle is the superclass of both Bicycle and MotorVehicle In our model
MotorVehicles have engines and license plates. Attributes have been added
accordingly, along with some behaviour that allows us to examine those attributes
MotorVehicles is the base class of both MotorBike and Car, therefore these classes
not only inherit the speed and colour properties from Vehicle, but also the
additional attributes and behaviour from MotorVehicle Both MotorBike and Car
have additional attributes and behaviour which arespecific to those kinds of object.