0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views1 pageCE2 A Guide To Problem Identification and Prioritization
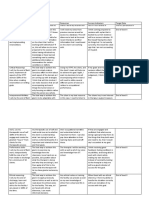
This document provides guidance on problem identification and prioritization for occupational therapists. It outlines steps for assessment, problem identification, determining which problems are appropriate for OT intervention, and prioritizing problems. Guidelines are provided for writing problem statements, including focusing on areas of occupation, performance skills and patterns, client factors, activity demands, and context. Levels of assistance and components for writing functional problem statements are also described.
Uploaded by
Charmaine Jerly NacarioCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views1 pageCE2 A Guide To Problem Identification and Prioritization
This document provides guidance on problem identification and prioritization for occupational therapists. It outlines steps for assessment, problem identification, determining which problems are appropriate for OT intervention, and prioritizing problems. Guidelines are provided for writing problem statements, including focusing on areas of occupation, performance skills and patterns, client factors, activity demands, and context. Levels of assistance and components for writing functional problem statements are also described.
Uploaded by
Charmaine Jerly NacarioCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 1