0% found this document useful (0 votes)
80 views4 pagesAudioFX Definitions
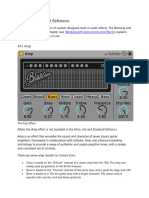
This document provides an overview of common audio effects terms and types. It defines core effects like delay, reverb, distortion, and modulation effects. It also describes various sub-categories of effects like algorithmic, granular, and resonant reverb as well as filter types. Finally, it outlines common effect control parameters for shaping the character of different audio effects.
Uploaded by
曲安琪Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
80 views4 pagesAudioFX Definitions
This document provides an overview of common audio effects terms and types. It defines core effects like delay, reverb, distortion, and modulation effects. It also describes various sub-categories of effects like algorithmic, granular, and resonant reverb as well as filter types. Finally, it outlines common effect control parameters for shaping the character of different audio effects.
Uploaded by
曲安琪Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4