0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views10 pagesAssignment 1
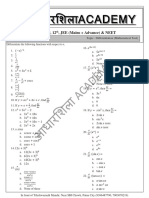
The document contains an assignment with multiple math problems involving calculus concepts like functions, limits, derivatives, and geometry. It asks the student to evaluate functions, find derivatives, solve equations, find slopes of lines, and analyze properties of triangles. The assignment requires applying concepts of differential calculus, analytic geometry, and trigonometry to solve the problems in detail.
Uploaded by
Hassan AlaradiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views10 pagesAssignment 1
The document contains an assignment with multiple math problems involving calculus concepts like functions, limits, derivatives, and geometry. It asks the student to evaluate functions, find derivatives, solve equations, find slopes of lines, and analyze properties of triangles. The assignment requires applying concepts of differential calculus, analytic geometry, and trigonometry to solve the problems in detail.
Uploaded by
Hassan AlaradiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10