0% found this document useful (0 votes)
127 views11 pagesArray Manipulation Java Examples
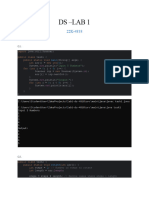
This document contains examples of array manipulation in Java including bubble sort, matrix display, array sum, finding the maximum element, swapping arrays, sorting arrays, binary search, filling arrays, copying arrays, and comparing arrays for equality. The examples demonstrate basic operations on arrays such as sorting, searching, summing elements, and copying/comparing arrays.
Uploaded by
rabexa4689Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
127 views11 pagesArray Manipulation Java Examples
This document contains examples of array manipulation in Java including bubble sort, matrix display, array sum, finding the maximum element, swapping arrays, sorting arrays, binary search, filling arrays, copying arrays, and comparing arrays for equality. The examples demonstrate basic operations on arrays such as sorting, searching, summing elements, and copying/comparing arrays.
Uploaded by
rabexa4689Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 11