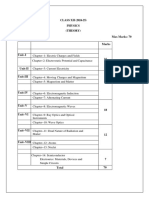
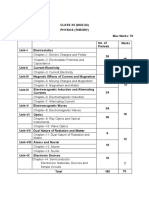
Chapter-1, Electric Charges and Fields
• Dielectric constant
• Coulomb’s law and it’s vectorial form
• Properties of electric field lines
• Electric field due to an electric dipole at an axial point of a dipole and at an equatorial point of a dipole.
• Torque on dipole
• Gauss’s law statement, proof (V. Imp.)
• Applications of Gauss’s law (V. Imp.)
1. Electric field due to an infinitely long straight uniformly charged wire.
2. Electric field due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet.
3. Electric field due to uniformly charged thin spherical shell (inside, outside and on surface).
Chapter-2, Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
• Potential due to a point charge
• Properties of equipotential surfaces
• Potential energy of a dipole in a uniform electric field
• Electric potential due to an electric dipole at an axial point of a dipole and at an equatorial point of a dipole (Imp)
• Capacitance of parallel plate capacitor
• Capacitance of parallel plate capacitor with a conducting slab and dielectric slab (V. Imp.)
• Formula of energy stored in capacitor
• Numericals based on series and parallel combination of capacitors
Chapter-3, Current Electricity
• Conductance, conductivity, current density
• Relation between current density conductivity and electric field
• Relation between drift velocity and electric field, derivation
• Relation between current and drift velocity, derivation (V.Imp)
• Effect of temperature on resistivity
1. For metals
2. Alloys
3. Semiconductor and insulators (V.imp)
1
� • EMF of a cell, factors affecting EMF of a cell, internal resistance, terminal potential difference (V.imp.)
• Kirchhoff’s rules Numerical specially (V. Imp)
• Whetstone bridge
Chapter-4, Moving Charges and magnetism
• Motion of charged particle in uniform magnetic field, both cases
• Biot savart law
• Applications of Biot-Savart law. (Imp.)
1. Magnetic field at the centre of a circular current carrying loop
2. Magnetic field on the axis of a circular current loop
• Ampere circuital law (Imp)
• Moving Coil Galvanometer, it's conversion to voltmeter and ammetre, current and voltage sensitivity(Ghot ke pee lo
)
Chapter-5, Magnetism and matter
• Dia, para, and ferro magnetic substances, Currie law
2
�Chapter-6, Electromagnetic Induction
• Faraday’s law
• Lenz’s law and Conservation of Energy
• Motional EMF
• Self and mutual induction (imp)
• AC generator principle
Chapter-7, Alternating Current
• LCR circuit and Resonance also Applications of Resonance (most imp)
• Transformer
Chapter-8, Electromagnetic Waves
• Displacement current
• Ampere-Maxwell’s law
• Nature of EM waves
• Uses of each wave of EM spectrum (V.Imp.)
Chapter-9, Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
• Real and Apparent depth
• TIR and its applications especially optical fibres (V.Imp.)
• Refraction at a spherical surface
• Lens maker’s formula and its numerical (V.Imp)
• Compound microscope when images formed at least distance of distinct vision and at infinity and it’s magnifying
power (V.Imp) numerical also
• Simple microscope when images formed at least distance of distinct vision and at infinity and it’s magnifying power
• Telescope
• Advantage of reflecting type telescope over a refracting type telescope
3
� Chapter-10, Wave Optics
• Huygen’s principle
• Reflection and refraction of plane waves using Huygen’s principle (Imp)
• Behaviour of a prism, lens and mirror on plane wavefront
• Interference of light constructive and destructive. Interference expression for intensity at any point in interference
pattern
• Young’s double-slit experiment (V.Imp.)
• Diffraction (V.Imp.)
Chapter -11, Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
• Experimental study of Photoelectric effect (V. Imp.)
• Laws of photoelectric emission
• Einstein’s Photoelectric equation and explanation of Photoelectric effect using Einstein's Photoelectric equation (V.
Imp.)
• De-Broglie hypothesis
Chapter-12, Atoms
• Observations of Rutherford alpha particle scattering experiment
• Distance of closest approach
• Postulates of Bohr model of hydrogen atom, orbital radius and speed of the electron, Bohr radius (Imp)
• Emission and absorption spectrum
• Line spectrum of hydrogen all the series
Chapter-13, Nuclei
• Mass-Energy, mass defect, binding energy, binding energy curve and it’s importance.
• Numerical based on Mass defect
• Nuclear reactions
CChapter-14, Semiconductor Electronics
• Distinction between metals insulators and semiconductors on the basis of band theory or energy band gap.
• Extrinsic and intrinsic semiconductor
• Energy band diagram of n-type and p-type semiconductor
• Barrier potential
• PN junction, forward and reverse biased
• I-V characteristic of p-n junction diode
• Half and full wave rectifier.