0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views23 pagesModule 5
Uploaded by
rohankakde200Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views23 pagesModule 5
Uploaded by
rohankakde200Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
You are on page 1/ 23
135
Module 5
Y_ Of Information System
SLL Introduction
Technology bas becoungs a uy
w the Business prareance ae vat
facilities are available
Wwaieed concept in the 24°
‘ 8s eomminnnic
WY AM Weots itheee
information. This intexesain eal
century and has brought about significant changes
Nieaion patterns across the global market. Improved and hi-tech
We Ns an hve made it easy for the user to transform data into
eee awemnitted in the form of files, reports, documents and confidential
‘Senn maniter because of improved information technology.
NAW aly
details over Varous
Standard and customised saan
Ase ave fs availale for Insinesses these days. ‘These applications integrate all
xtuct the Dest and Ooo aa ty ete, Theye ative can then be monitored by experts who always
ae ¥ SE SON seth intonation hy selecting the required information through various processes
'S. The use of Gus Qype of sothwane aids the management in evaluating Return On Investment (ROD.
ceded in the available hardware in an organisation to ensure that the
SS compatible and operates in a successful manner. The configuration of information
she husis of a blueprint so that the entire process can be carried out by following
jementing the information system in the real time scenario.
speci
The toil bow technology helps organisations to get a competitive advantage:
helps to overcome geographical boundaries.
nt is made easy.
wn and format is more efficient.
cement is maintained.
‘ble,
Dambase
Informacica
y information system application is to design modular and hierarchical steps of
‘generated in a report format in order to provide information that has some value
2s follows:
2) Transaction
3) Application Process
4) System Proce
t
5.1.2. Data Processing .
Pata comes fen tm Lin glural nnd "satu". Dal is any fac or igure that is collected by experience,
experiment on cbsar vated HH CLMPINEE BySIEN
v vk ‘hich
According to travis, ‘ls, How nuleval for information, is defined as groups of non-random symbols, wi
pet iit sefiohs, shjesto, ste. Dati item in information systems are formed from the characters.
‘These ray be alphabet, minis, HF apseral symm”
When data is processed, i gives icwvingtul information. Pata on being processed and presented in
meaningful manner te thie end ues 18 Kanye as Information,
Piyssesing FHP] formation
136 MBA First Semester (Management Information Sytem) Kya
: i ce is known as Data Pro
The data that has been captured and encoded in a specific format when Drocessed i eting
System. It has been stored in some other unit of an information processing System
data and convert it into use!
ter before processins
1 make
ul information. Data needs to by
Data processing is also calle
it more usable and meaninggy)
Data processing consists of methods that take raw
collected, checked for accuracy and entered into the compu
as information processing. Data processing is the act of processing data (
it can be converted into information.
so tha
1.2.1. Method of Data Processing
‘There are two methods of data processing: soak i i
1) Manual Method: The method of processing data and converting it into useful information ‘takes place
without the use of electronic devices is known as manual method. Hand and mechanical devices are used
essing of data,
issued, books retuned, calculation
od is an ancient method of data
There may be some mistakes in
e for data processing.
or example, a clerk in a library maintains details of books Til
in a register by writing the required details. Manual methi
ind is losing popularity because of the disadvantages it ha
‘manual method data processing. ‘This method isa slow and takes a lot of
of computers and other electronic devices is
2) Computerised M
a ly manual and partly electronic.
known as Electroni
ethod: Data processing that makes us
ing (EDP). EDP may be
ing has many advantages over manual methods. Thi
es the speed of data processing.
method reduces
5.1.2.2. Steps of Data Processing
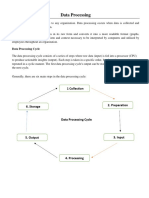
‘The following are the steps involved in data processing
1) Collection: Data collection is the first stage of data processing and is very important because the quality of
ta collected has an impact on the output. The collection process needs to be carried out in a manner to
that the data collected is slefined as well as accurate so that the subsequent decisions made are valid,
ens
‘This stage provides a bene
Some methods used for data colle
i) Census (data collection about several things in a group or population),
ii) Sample survey (data collection for only a part of population) and
iii) Administrative by-product (data collected ss a by-product of daily operations of an organisation).
2) Preparation: This is the stage in which data is manipulated into a suitable form for further analysis and
processing. Raw data cannot be processed and needs to betchecked for accuracy. Preparation involves
Contstruction of a dataset from several data sources so that the data can be further explored and processed.
Analysing data that has not been carefully sereened! and prepared can produce misleading results,
3) Inputs This is the stage in which the data prepared is coded into a machine readable form for processing by
8 computer, Data is entered in the computer using an input deviee such as keyboard, digitizer, and scannet |
from an existing source, Data entry is a time-consuming process and requires speed and ‘accuracy. ‘The data
that is entered must follow standard syntax because a highly skilled processing power is needed t0
breakdown data at this stage. The data entry is a costly process and th :
many businesses are outsourcing this stage. a sa is'one ofthe main reasons, wh
4) Processing: In the processing stage, the data is subject to various met ipulati
program ‘hat contains a code and curent activity 3 executed at this oe ene acuaion, compa
Inultiple threads of execution to simultaneously execute instructions depending on ine aaa en en A
Computer program isa passive collection of instructions whereas a process isthe nurear ne oc
instructions. Data processing can be done using any program from the larg execution 0}
¢ numbe le
these days, These programs complete data processing of large volumes of data ina of propane availabl
a stage, the cessed information is
5) Output and Interpretation: inthis stage, the proc nation is made availabl.
fe presented in several formas ikea printed report audio ot video report et. The ou my provided reds tO
be interpreted so that it can provide meaningful information to user for guiding them for future Hecisions
oon the basis of which to measure as well as focus on what to improve.
at
qestnlogy of lnormation Sytem (Modus
l-5)
6) Storage: In this last stage’ i"
Storage stage allows for enc ttt Processin ;
f allows for quick ssing, informa a
various memory devices - sees: and reieval of i eee he fas Lani
eonpaie ste For the storage of data, the
5.1.2.3. pes of Data Processin;
Data processing is of two typ. ®
‘Types of Data Processing
Batch Processing System
LJ Ontine Processing
1) Batch Processing Sys .
system: "
processing of data is requi ee this system, data is gathered and processed in batches or groups. Online
proceasing in een in interactive business systems for immediate data input and output ‘but batch
ssing is a ie ee systems can be used for several other purposes. For example, batch
ly used for processing large amounts of routine data like pay-checks or credit card
rocessing this file, For example,
Beet preceating involves! i
atch processing involves grouping input data into a single file and then ps
processes customer
pee application may process thousands of records in a single run when a firm
statements at the end of the month.
update of records is not
atic job-to-job translation
Batch processing is an appropriate process in applications where immediate
required such as payroll. Today's most ofthe operating system provides autom:
service, Batch processing system based on this service of OS.
“The main characteristics of a batch processing system include:
i) Collect, group and process transactions after a period:
i) Batch programs can be run ofa pre-determined schedule without user involvement at any time and
iii) Batch processing needs less network resources as compared to online processing systems.
Steps of Batch Processing:
Step 1) A computer operator collects the source anneal programs collected on forms, These forms are
grouped in a batch and a patch slip is attached to it. The batch slip contains information such as
Jescription of documents, number of ‘documents etc. Next this batch is sent to the data processing
entre for processing. The batches are validated against the batch slip and the data is stored on
storage device such as hard disk.
Step 2) The operator loads the validated batch of programs into the computer. These batches are then
a ted sequentially. The execution updates the maser file and then generates final reports.
Step 3) The printed reports are ‘gathered by the operator and then distributed to their users.
‘Advantages of Batch Processing
Aaytallowing are the advantages of atch processing:
1 of computer resources among several Users.
i) Itallows sharing
i) The time of job processing is shifted 10 when the computer resources are not (00 busy.
} It prevents the idling of computer resources
Disadvantages of Batch Processing
‘The disadvantages of batch processing include:
J he data may be destroyed or damaged when being cumulated into batched. a
Every job has to wait at every step thereby inereasing the tumaround time.
iit) Desired priority scheduling is not possible.
2) Online Processing: Early computer systems made use of batch processing but most computers today make
ase of online processing. An obline processing system handles transactions whenever they occur and
provide output to the users directly. An online processing system is interactive and therefore avoids delays
and allows users to constantly interact with the system. hs
¥
138 MBA Fist Semester (Management Information System) RTMNY
, a user can enter the ori
For example, an srline reservation system is an online processing s¥S00 a en US bales na
destination, travel date as well asthe travel time onthe soreen. The systom them seve Te ts and
displayed the available flights and their schedule on the user's request, The Swarts San ake a
reservation online by entering the detail ike name, addres, credit card information ad Any hes data
required by the system. The online system then reserves and assigns @ Se
the flight database immediately. aerate
sing of checking acc
It can also be used with file based systems. Figure 5.1 shows the online processing of leCKINg, ount
balance by a customer in ATM.
After that ATM verifies th customer's infomation ike debiverdit card and password the eutome ens the
request. The system then considers customer account number as the primary key era a a
information from account master file. The account number is verified by the system and the details are displayed
on the sereen of ATM. The system transmits the information to the ATM which then prints it for the user.
ge ATM Query Process
[1G “etsorrencs
account balance
Online Step 2: Retrieves current account
Processing balance
System
Step 3: Verifies bank account
‘number and displays balance on
‘ATM screen
Figure §.1: When a Customer Requests a Balance, the ATM System
Verifies the Account Number, Submits the Query, Retrieves the Current
Balance, and Displays the Balance on the ATM Seren
Advantages of Online Processing
The following are the advantages of online processing:
i) It makes easy to shop online,
Online systems have quick response time.
iii) Form filling and processing jobs is very easy and these can bé done autor
servers.
iv) Money transactions are done using online processing systems by banks,
v)_Usages of Credit cards are controlled by online processing systems,
matically by web and database
Disadvantages of Online Processing
‘The disadvantages of online processing are as follows:
i) There are thousands of request that may take place at an;
ii) Ifa server hangs during a purchase being made, the process gets intemepne :
organisations ited Which is not good for big
ii) All important data like bank information, creditcard details ee, are stored on a genes
gets hacked, all infomation gets loosed. For example if Linkedn account eon eon ttf the system
acces to all users" ID and passwords ad the credentials or other importants kee hacker gets
misused by hackers. of these users can be
‘Any hardware failure results in the transaction being interrupted and .
x saan na - . Stopped leading to inconvenience
vy) An interruption in the power supply to the online processing systems can at
» transactions and soi is important to have the backup of elecrc power suppiye oe fale of several
y given time making it difficult to handle them.
centony of infomation Sysem (Motu.
si) Online processing system
wii) Its essential for banks 1
banks can handle it immedi
vill) Transferring products to
lot of personnel, time anc
require a »
be alen i
ately.
People physically in a
d cost, ly in an online processing system is a problem and involves @
ix) Many users also face issues when
s i rel
Ssues when creating new accounts in onli
ine processing systems.
51.3. Transaction Processing
one of the earlier computerised
oor, process, validate and Systems was Transaction Processi
P a store trat jc tion Processing System. The se of this system is t
lot of
elie ane? Mate inventory and ter process
ing at all times so that if some problem occurs, the
Transaction Processing System (
produced bythe execution of ae is cross-functional information system that processes data which is
formation system that records cory actions. ‘A Transaction Processing System (TPS) is one such
Dear nrt tasintes Unie"! Roo \pany transactions wherein a transaction is an exchange between any
sa able seats, Tis i iene example, in case of the ticket reservation system, TPS data contains location
eae eee the terminal which indicates the sold out seats. Once a
ee erp ee and may be a mailing label, for sending tothe customer. Similarly, in the
TPS shows data of available products with their prices and related data.
‘Two types of outputs are generated by TPS program:
1) Itsends message back tothe operator terminal.
2). It generates printed documents. "
Notice of event
aH een HE
keyed || me Data
Figure 5.2: rchitecture of a Generic TPS Application .
5.13.1. Features of ‘Transaction Processing System
Primarily, there are four features of a Transaction Prowsss-t System:
1) Rapid Response: Customers should not be kept waiting. Faster the transaction, happier is the customer:
‘This leads to more revenue generation, as ¢ satisfied customer in all likelihood will be a regular customer.
2) Reliability: As this system involves ‘cash, there is no room for mistakes because it has a direct impact 2
customer satisfaction, audit, taxation, el
3) Inflexibility: Since the system involves money, a rigid set of rules is required for transaction processing. The
ni eet of rules should be followed every me. "An alteration in rls will increase the chances of mistakes.
Id be in place to check that everyone is doing the right thing. For
4) Controlled Processing: Procedores shou
comransaction processing monitor should check Thether everything is right with TPS or not.
5.1.32. Types of Transactions
Sr 32s that occur while doing businesslike sales, purchase, etc. are known as “Transaction”
‘Transactions can be of to tyes:
Ty titemnal Transactions: Those transactions which oreo the time of internal working of the company such a8
‘the Recruitment Policy, Promotion Policy, Production Policy, ete., are referred to as internal transactions.
For example, when the accounts department orders stationery from the purchase department, then itis an
internal transaction.
2) External Transactions: Those transactions which are related 0 extemal sources for procurement are
eat dered a external transactions. For example, when a customer places an ‘order for a product, then itis
an extemal transaction.
nd processed at regular
Where data processing and
rinsaction processing
Pre-specified formats or screens. For
'ecount or the status of a sales order and receive
5.34. Advantages of Transaction Processing
selling the goods and services to its customers.
“rent patiems, Which are concurrently added by users.
foduced by users, then TPS provides the faster
at
save the server
redundant
5.1.4. Application Processing
ion processing stage
status, One can change
consisting of usc!
signed for various purposes Tike for statu
1 example, if the numbers of work orders are
e wide is differen
Mf status triggered actions in related fields
hold then no materi {js available for processing.
‘ons which are mostly affected.
5.1.5. Information System Processing
h sing system, the speci
structure would be differe
1) Trial balance,
2) Balance sheet,
4) Payable and rec
5) Expense analysis etc.
Hence the chart of account for every business would vary depending on the type of business.
A nforation processing system (or Information Processor) takes information in one form and processes or
irnforne origaton into another form. For example, when the customer billing data are processed for
nancial accounting and customer's credit rating, then it is considered as a commercial system.
in system processing, two ot more applications are processed together to provide the efficient results,
a MBA First Semester (Management Information System) RTMNU
For effective information processing, it is essential to have a formal system that:
1) Handles large volume of data. : i
2) Validates the data and confirms transactions.
3) Handles complex processing of data and also carried out multidimensional analysis
4). Performs quick search and retrieval
5) Allows for mass storage.
6) Communicates with the user on time.
7) Pulfils the changing needs of information.
‘An information system structure can be understood with the help of its proce
processing functions of an information system are as follows:
1) Process Transactions: Information systems process transactions a
2) Maintain Master File: Information systems generate and maintain m:
3) Produce Reports: Information systems produce reports as outputs ‘These reports
daily basis and known as scheduled reports.
4) Process Interactive Support Applicatio
that allow the users to interact with the sy
ONLINE ANALYTICAL
5.2.1. Introduction ee
Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) isa method of analysing data in 4 multi-dimensional format, often across
multiple time periods, with the aim of uncovering the bu information concealed within the data.
an activity of an orgs
aster files that store
historical data.
‘may be produced in a
~ Information systems also need to process SUPPOT applications
em.
PROCESSING (OL
‘According to EF Codd, “The dynamic synthesis, analysis ‘and consolidation of large volumes of
multidimensional data’
LAP uses Multi-Dimensional (MD) views of aggregate data |
OLAP of possible views of information and transforms raw data
to reflect the enterprise a rs and Executives. In addition
to vering who and what questions OLAPS can answer “what if” and why ‘Thus, OLAP enables strategic
aoe yemaking. OLAP calculations are more complex than simply summing data, However, OLAP and Data
deeisrrvtes are complementary. The data warehouse stores and manages data white the OLAP transforms this
information.
10 provide access strategic information.
ables users to gain insight to a wide variety
‘understood by the user, for example, Analysts, Man:
dat
OLAP tools are based on a multidimensional data model, Multidimensional data model is an integral part of
ort ine Analytical Processing, or OLAP. Beciuse OLAP is on-line, it must provide answers quickly; analysts
pose iterative queries during interactive sessions, not in batch jobs that run overnight. And because OLAP is
rr analytic, the queries are complex. The multidimensional data model is designed to solve complex queries
jn real time, The multidimensional data model is important because it enforces simplicity.
10 strategi
Using OLAP, the manager can access the reports to be analysed without giving the instruct
= ‘ struction to pros ers
to provide him the report OLAD isthe most popular technology and it forms the base of Execution Information
Sputem (EIS). Senior managers can view the extracted multidimensional data into graphics and table form f
ddata analysis using the OLAP. Eraphics and table form ive
5.2.2. Features of OLAP
‘According to Business Intelligence Ltd., OLAP can be defined in fi .
Dimensional Information (FASMI). in five words-Fast Analysis of Shred Multi-
Features of OLAP
Fast
Analysis
‘Share
|_[Mattidimensionat
Information
Technology Of Information ¢,
System (Modus
ules)
1) Fast: Fast means that th
the simplest anal atom targeted to de er ibout five second,
lysis takin, re tha deliv
ne ; 18 no m ‘Most responses to user within about five s
is: an one second and very few taking more than 20 seconds
in 20 seconds.
143
»
cope wit i i
the user, keep it oa ae logic and statistical analysis that it
re: Shar a 5 the target user,
multiple write access ig nests S¥Stem im
sera to write di ae a 7 led, concurent as a the security requirements for confidentiality and, if
Updates in a timely ace BU To the growing toa tan appropiate level not al applications need
imely, secure manner. '€ number that do, the system should be able to handle multiple
4) Multidimensional: “Mutidimens 7
onal
multidimensional conc
most logical way to a
3) Share: Share means th
eptual view of te di the key requirement. OLAP system must provide a
° nalyse business and on See full support for hierarchies, as this is certainly the
5) Information: Information is all of ;
much is relevant for th of the dat
© applicat
much input data they can fendi vies
52.3. Types of OLAP
‘The major types of OLAP are:
1) ROLAP: R stands for Relational
response times can be slow. All c:
‘a and derived information needed? Wherever it is and however
are measuring the capacity of various products in terms of how
many gigabytes they take to store it.
~ calculations are done in a relational database and so with large volumes
alculations are pre-generated when the cube is populated.
ROLAP supports large dat i i
See i aa eae enabling good performance, platform portability, exploitation of
ry rocessing, robust security, multi-user concurrent a¢ ‘includi ad-
write with locki ont ‘ys er rent access (including reac
fenilie, rove in). recognized standards, and openness to multiple vendors’ tools. ROLAP is based on
+ proven, and already selected technologies. The architecture of ROLAP is shown below:
Database Server ROLAPSener | Info, [Frontend Too!
sau.,| Request
a |
, L_.
= a al
Figure 54: ROLAP Architecture
Advantages of ROLAP
i) Relational OLAP tools can perform more robust types of analysis than multi-dimensional OLAP,
incorporating a wider range of data views
ii) It supports flexible analysis, i.c., the analysts can explore the data in an ad hoc fashion
iii) Tt allows multiple multi-dimensional views over the same data tables, o support different business areas
iv) Itcan support large volumes of detailed data for "drill down" analysis
¥) The processing load can be shifted onto a server platform, allowing these to be used with network
computers or over an Intranet or the Internet
vi) There is no requirement to rerun aggregations when additional data is added tothe relational database,
Disadvantages of ROLAP - ; / /
3) Using relational databases for multi-dimensional analysis can lead to performance issues when data is
extracted from the database, ifthe database is not well designed
ii) ‘The denormalised database design gives rise to substantial data redundancy
iy Many relational OLAP products do not provide the same degree of data visualization found in multi-
dimensional OLAP tools. : sine gti HAS
iv) Releonal data structures require more time for simple OLAP analysis than inult-dimensional OLAP
tools because the data must be extracted prior to analysis.
EE
isnput
powad Zurita pow woneaHSSeT
1M se Yons
I fen Hons SUISUN ysKo8 fa pamseow mp oes AUD i Jo SAI 2
Hine ran garsuanr asinosai suoddns dVT0 PHVsH
nu yI0q Jo s
you st 0} Timp yarn Jan9q 21p auiquios o1 wi998 stonposd WTO PHAAY 9ouE|s ISIN
aun ‘sisKjeue ,.usOp up, Su 1) aseqerep [euoneyax amp wosy erep [seIAP Sursqsapun amp wrEIgO WEI
» Supp Ayosesoy us auf Jo wong amp So4se—u ISATEUE Oy) UMA
-asvquiep yeuoneyas & ur viep aaumos Bul
wu ASojouysar wawradeuvur asequiep
yuvarud sionposd av10 PHASH FAV'10 PHOSH (€
‘ssaseqerep 230] 01 parins rou axe Koy (14
no ayn 01 Poppe s!
‘yep Mau WY SUN As9A9 sUONTaIe oy Jo [[e aye[NoTeD-01 0} juDUIaZIMbaT ‘sopssoand reat 4 fF Toit (a
surayss wuawaBoueus aseqewep [2 nymu odds 01s:
‘s]00) saM9} axe a10yp swa}SAS yUoWIeSLURI asequIEp [PUOTEIAY 105 ‘uerp samo] Yoru st aseq sosn ay sy (8
ws ou pure yuouxdojaaap a Sursvasou sayy ‘S@seqewep
ouo|suounpnynar ureuteur pue pling oF siyjoor puE STIS mou aunbos qm wauuedsp LI AL (AF
(dde spsdyeur Aue Xq pasinbos
lumop |]uP.. 01 mnowyip af soul wIEp ax JO sumeL poreSousse oH,
pazjue8109s 2q 01 paau Keus oqno wiep axp *(evep J9UH0ISNO
po idurexa 40}) aBueyo swwourasynbos woxsuouyp SUAS
{yo smaqa wary *°t‘asequvep a0 ayp Wrox} StOzE
"yovezary woIsuauuip Hynur axp Jo sumiew apgpsoyus LL Ct
“AVION Jo se8eqUEAPESI.
ayy 01 BIEp [euOsUAI
ys aBesors rawp [et
NU uN] 01 sassautsng smo}
auuIp-Nynus pastperoads ayesa
“a9 01
nap Tuyspopun oy OF ,
oy woIsuoMp v se poyrou yuouIAed
ssautsng ajdnynut woddns or Ange 2m
2 Fuipring pue suonejnaqeo Suywws9ps0d
Sussaooxd Azonb Suumnp suonwedas33
s Price list ~
Le ror
Ce men
Sales evn a so sery
manager
‘Terminal register
Figure 8.7: Online Real-Time Processing (OLRT) "
1) Business Event Occurs and Record Business Event Data: At the time of the business event, the
into the system. Source documents are almost never used because they
significantly slow the process and remove some of the advantages of non-redundant data entry. Noti
that he dt nity poses where the sale in entered into the system isthe same as in figure $8 (other
than the absence of the filed copy of the sales receipt). Thi :
iia he PY This is consistent with the use of OLTE for
uname ne
eon
cust s.
BZ
ze
EB
Re
Processing Favironmment)
4) Update Master Data: Esch bs
gay ealculations and sar
Generate Reports (and Support Queri
each business ev
‘books and CDs store,
cases, rather than using Pre
makers need, these information systems users ly
provide the one-time information they need vnake key decisions. For example, the
mun report on the jnventory stock for the 10 top-selling ‘CDs and books.
iminate the delay
the cost. To
will use a query Ianguage
to-date information. However, the
'y operate an OLRT system, it is
computer system — ie. online.
OLRT systems allow users to nearly
primary disadvantage of real-time system
imperative that the point of the business linked directly
‘Accordingly, to operate an OLRT system, ‘OLTE methods must also be used
sms that use the periodic mode. Although the data entry
the mode of processing may vary. Whereas @ pure
nig in batches, an OLRT system using OLTE processes
business event data cannot be aggregated a 2
each business event must be
expensive approach to OLTE.
jon to download the data to the
‘onic communication connection that
communicated for processing at the time the eve
Inessence, rather than creating a temporary electror
central computer, an OLRT system generaly red
vill usually necessitate the use of some form of network.
‘Automated systems that model manual systen's ‘and OLRT systems are the Qwo extremes in business event data
Processing, The systems that mimic manual systems are what we m pure periodic mode systems in that
2 delay occurs between every step of the processing. On the other OLRT systems represent pure
that litle oF no delay occurs between any steps in the processing. We mote these as
immediate mode systems in
mes by exhibiting a mix of periodic
formation System) RTMNU
152
cessing Fesults in an
data steps, Whereas
For example, OL
and immediate mode processes
sss event occurrence and record eve!
immediate mode approach for com
periodic mode processing
5.4.3. Advantages of OLRT
1) Data entered directly into the inforn
2) Transactions are processed indiv
3) Allows reports and queries
occurs.
5.4.4, Disadvantages of OLRT
inecring (CASE) tool refer to automated
enanc
CASE can be used to automate some fu
‘As market demands are changing at a much faster pact
faster so as to replace old products with new ones. So, in order
process, CASE is introduced.
of processes and artifacts of
2, etc.
CASE tools (software pro
software engineering. They help
5.5.2. Reasons of Using CASE Tools
One of the main reasons for us fe
1)
po)
3) Delivering continuity between the phases of the life cycle
4) To evaluate the influence of maintenance
5) Lowering the cost of repetitive manual act
6) Lower the development time of the project and
D
8)
ion
5.5.3. Characteristics of CASE Tool
A CASE tool should have the following charac
1) Standard Methodology
Testing Software: CASE tools
4) Integration
and other testing software under cl
helps in regres
&
‘ech
rt for Reverse Engineering: CA: ,
Support for | '8 CASE tools should be as that it can create
models from
Ip: CASE tools offer online tutori
5.5.4. Architecture of CASE Envi
‘The below mentioned arc!
1) A database for storing inform:
‘ironment
ponents are part of a CASE tool:
A,
3) A tox
4) Auser
User Interface Layer
Tnertace ToolKit
Presentation Protocol nie Teal
= ST
‘Tools Management Services
cast
Tool
Layer
Layer
ration Services
Management Services
ibrary which contains
agement of interface between human and computer,
CASE tools and components ean communicate with each
use and keyboard, menu names,
to manage the tools are als
led by the Tools Management Sei
sk communication and synchronisation in case m i is performed by
¢. This is done by gathering metrics on the usage of the to
een the repository and management system to the tools. The auditing and security
also completed by it.
3) Object Management Layer (OML): The configuration management tasks are performed by
mechanism is
MBA Fins Semester (Management Inform
OML also support change
the task of classifying
1st
repository by this set of standard modules. Apart from all these functions, the OM,
cenira, Matus accounting and audits, Configuration management services such as
those configuration objects that perform version control are also ‘executed by it.
help of which the object
with the ;
inctions Mayer. Shared repository layers
4) Shared Repository Layer: It is made up of those access control fu
‘management layer interacts with the CASE database that is present in th
and object management helps in attaining data integration.
benefits can be obtained
5.5.5. Advantages of CASE Tools
‘Though it is possible to achieve benefits if CASE tools are
from the CASE environment. Following are the advantages of CASE tool:
1) The process system has an effective and longer operational life,
2). The produced system fulfils the user's requirements more efficiently,
3) The documentation of the produced system is tremendous,
4) Requirement of the support in the produced system is very low, and
ted, a great number of
5) More flexible systems are produced.
5.5.6. Disadvantages of CASE Tools
CASE has the following disadvantage
1) The systems that are produced primarily requi
more perfect and extensive definition of the user's needs,
cost to maintain and build,
grea
2) Itrequin
3) Customisation is difficult
4) Trained maintenance staffs are needed, and
5) Difficulty is encountered while using with present systems.
5.5.7. I-CASE
lools are also known as I-CASE or Integrated CASE. Every the aspects of the SDLC are covered by
also cover the several aspects of
CA
T-CASE tools such as writing code, implementation and maintenance. It
sofiware engineering such as managing, modelling, error-testing, designing, prototyping of system model
etc
CASE tools can be categorised as upper CASE tools and lower-case tools. In this, the upper-case tools usually
Juding the planning of goals. In this stage, the necessary
‘emphasise on the starting stages of the development
information is collected and through the tool, itis presented systematically,
On the contrary, Lower CASE tools emphasize the later parts of the process growth including designing, codit
sou testing of software, its defete and funecuonaiy. Testing and maintaining the product plays a huge role in
the development of software.
Integrated CASE tools offer the organisation to create a bridge between the upper- and Lower-Case tool:
Z s.
Therefore, it can be said that CASE tools are incorporated within the
7 ‘ rs "
which can help in sharing the representations of the system even ‘sea ie ‘aia va aia
carry out format
conversions.
Hence, to ease the transfer of information between dif \
repository for all the tools. ‘rent SDLC phases, I-CASE needs to use a general
‘The prime element of CASE environment is a centralised
: é 4 database
various tools utilised during the SDLC stage are inte; oF repository, with th |
¥ fui: ited, 7 ie hel;
developing, modifying and developing software from its fist stage sy Ce, OF information 7 sired fot
are stored in the repository. Be (0 the generation of code and meintenanee
“nance
canon tron Sys Mat) :
spissilostated in the figure 5.10,
Figure $10: Mstration of System Development ems Stored in the CASE Repository
Each CASE tool utilises a common repository during the entire lifecycle. The automated environment that eases
the growth of information systems can be referred to as both I-CASE and CASE. For developing information
systems that are not dependent on the CASE tools, a common repository has been used in the past.‘The different
parts of a complete repository are shown in figure 5.11.
Alcan Development Production
Evironment Environment
—
‘CASE Tools “opane
Reposiory
Information Repository
Data Disionary >} 1) Business Information
2) Application Pototio
Figure 5.1: Mlustration of Common Components of a Comprehensive CASE Repository
However, the platform in which the end-users utilise CASE tools, high-level language and many other tools is
known as the environment of application development. Whereas the platform in which people create databases
and update data with the help of applications is known as the production environment.
Two main divisions of a repository are as follows:
1) Information Repository: It is responsible for controlling and maintaining the business information, ‘The
business scope of an application is combined with business information using this repository. Business
information is generally stored in the corporate database whereas application programs are managing
business information with the help of repository.
2) Data Dictionary: Organisation data and its corresponding resources can be accessed using the software
tools known as data dictionary. Any modification to data dictionary can impact programs, forms, diagrams
and reports in I-CASE. Entries in the data dictionary are standardised and their detailed description has
following properties:
i) Element name and corresponding aliases inclusive of data entities and programs
i
i ay
TM
6
formation
CMtanagement tot
located in L-CASI
ystem (DBMS), repository |
on among th
es. It provides
nodel,
ferent factors of it?
vcessing?
pes of data processing,
processing system,
4 socessing? Explain the features of T
5) What are the different types of transactions? Write the steps of
Discuss the benefits of transact
a processing’? What are
/? What are the main features of OLAP?
are the advantages of OLAP?
LAP? Discuss the problems o
Discuss the elements of TOM.
‘stem. What the sub-processes of online real-time
13) What are the advantages of real-time system? Also discus.
414) What do you understand by CASI
15) What ae the main
46) What is -CASE? Wh
iypes of OLAP.
10) What are the different ateas of applications o
ementation of OLAP,
mation system?
ime system,
disadvantages of rea
sls? Discuss the reasons of using CASE Tools
* Explain the architecture of CASE en
0f CASE tools?
‘ronment,
MODEL PAPER- |
MBA - FIRST SEMESTER EXAMINATION
‘Max. Marks: $0
ual marks,
formation system.
Or
py What are scorecards? Discuss Balance Score Cards in brief, ti
2) «) Whatare applications of MIS in manufacturing sector? Ih
Or
'b) What do you mean by production management? Hustrate the model
lustrate the model of Information processing system.
of protuction information system,
(16)
b 6)
4 06)
rn n. Explain about the ERP Model and Modules. (16)
5) 9) Whatis data processing an transaction processing? What are the limitations of Transaction prcesing? 46)
8) Whatis Online Analytical Processing (OLAPY? Discus about the different types of OLAP. What are the advantages of
OLAP? 6)
MODEL PAPER- II
WENN SUT oe ea
MBA - FIRST SEMESTER EXAMINATION
‘Max. Marks: 80
erations and business performance? What do you mean by strategic design of
6)
Or
janagement of business? Elaborate the concept of corporate planning. Explain strategic planning in detail. (16)
te the model of Personnel Information system.
lain process of Hotel management in detail
Or
3? What are major modules of Banks
Management System? Describe Insurance Management
) Discuss about ERP and SCM, What isthe benefits and limitation of ERP?
Or
') What is CRM? Write the processes occurred in CRM. Explain the areas of application of CRM? c
a) What is real-time system? What the sub-processes of online real-time information system? Also discuss spot te
advantages and disadvantages of real-time system.
Or
i 2 imitations gf CASE too
) What do you understand by CASE tools? What is LCASE? Also discuss the benefits and limitations et
You might also like
- Information Technology Infrastructure Module 5No ratings yetInformation Technology Infrastructure Module 523 pages
- Define Data Processing? Answer 2. What Are Data Processing Activities? AnswerNo ratings yetDefine Data Processing? Answer 2. What Are Data Processing Activities? Answer4 pages
- Business Information System Notes - Theory - PhoenixNo ratings yetBusiness Information System Notes - Theory - Phoenix46 pages
- Business Information System Notes - TheoryNo ratings yetBusiness Information System Notes - Theory93 pages
- Registration No: 12Pmm417 Name: Maulik PatelNo ratings yetRegistration No: 12Pmm417 Name: Maulik Patel25 pages
- Chapter 3 DATA Processing and Computer Application0% (1)Chapter 3 DATA Processing and Computer Application31 pages
- Terminal Remote Company Interface Internet Website Product Orders Dealing Payments Offers Savings Efficiency Business Sales Operations System TermsNo ratings yetTerminal Remote Company Interface Internet Website Product Orders Dealing Payments Offers Savings Efficiency Business Sales Operations System Terms4 pages
- Data Processing and Management Information System (AvtoBərpaEdilmiş)100% (1)Data Processing and Management Information System (AvtoBərpaEdilmiş)6 pages
- Information Processing: Ten Skills Used To Create A BrochureNo ratings yetInformation Processing: Ten Skills Used To Create A Brochure3 pages