0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesData Processing
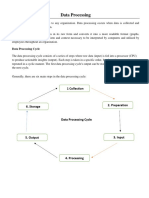
Data processing involves converting raw data into meaningful information through a series of stages, including collection, preparation, input, processing, output, and storage. Various methods such as batch, online, real-time, and distributed processing are utilized to handle data efficiently. Additionally, file access and organization methods, including direct, sequential, and random access, are essential for effective data retrieval and management.
Uploaded by
simonwambua886Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesData Processing
Data processing involves converting raw data into meaningful information through a series of stages, including collection, preparation, input, processing, output, and storage. Various methods such as batch, online, real-time, and distributed processing are utilized to handle data efficiently. Additionally, file access and organization methods, including direct, sequential, and random access, are essential for effective data retrieval and management.
Uploaded by
simonwambua886Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4