0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views26 pagesFire Protection
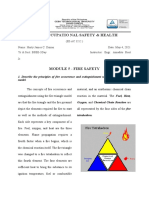
The document discusses fire prevention and protection in the workplace. It covers requirements for escape routes and exits, emergency action plans, fire prevention plans, fire extinguishers, and workplace fire prevention tips. Specifically, it outlines that employers must provide proper exits, firefighting equipment, and employee training. Escape routes must be clearly marked, illuminated, unobstructed, and unlocked to allow quick escape. An emergency plan and fire prevention plan also must be established, and fire extinguishers properly inspected, maintained and employees trained on their use.
Uploaded by
sonficyusCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views26 pagesFire Protection
The document discusses fire prevention and protection in the workplace. It covers requirements for escape routes and exits, emergency action plans, fire prevention plans, fire extinguishers, and workplace fire prevention tips. Specifically, it outlines that employers must provide proper exits, firefighting equipment, and employee training. Escape routes must be clearly marked, illuminated, unobstructed, and unlocked to allow quick escape. An emergency plan and fire prevention plan also must be established, and fire extinguishers properly inspected, maintained and employees trained on their use.
Uploaded by
sonficyusCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 26