10/29/2023
ENERGY CONVERSION
Lecture 4
PV system architecture
Content
1. PV system architecture
2. PV system components
o Charge controller
o Inverter
o Battery
1
� 10/29/2023
PV System Architecture
Stand alone system
Hybrid system
Grid connected system
Stand alone system – direct
connection
oVery simple architecture
oLimited to only DC load
oPV not operated at MPP
2
� 10/29/2023
Stand alone system with battery
Why need battery?
3
� 10/29/2023
Hybrid system
Hybrid system
4
� 10/29/2023
Grid-connected PV system
Grid-connected system – 1
10
5
� 10/29/2023
Grid-connected system – 2
11
Grid-connected system – 3
12
6
� 10/29/2023
Typical layout of a utility-scale
PV system
13
Content
1. PV system architecture
2. PV system components
o Charge controller
o Inverter
o Battery
14
7
� 10/29/2023
Connection of charge controller
15
Functions of charge controller
oMain role is to control charging and discharging of the battery
oOver charge protection
oOver discharge protection
oMonthly equalization charge
oVarious controlling mode for load
oOver temperature and overload protection
oShort circuit protection of load and PV
oReverse current protection at night
oReverse connection protection of PV, load, and battery
16
8
� 10/29/2023
PWM charge controller
17
MPPT charge controller
18
9
� 10/29/2023
Maximum Power Point Tracker
19
Types of charge controller
20
10
� 10/29/2023
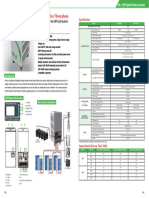
Example of a MPPT charge controller’s spec
21
Content
1. PV system architecture
2. PV system components
o Charge controller
o Inverter
o Battery
22
11
� 10/29/2023
Solar PV inverter
❑Solar PV Inverters convert the DC output of photovoltaic
(PV) solar panels or strings of panel into a AC current
which is injected to the grid (or load).
❑Solar PV inverters have the following functions:
◦ DC/AC conversion and voltage adaptation
◦ Maximum power point tracking
◦ Anti-islanding protection
◦ Synchronization with the grid
◦ Support to the grid where the PV system is connected
23
Inverter efficiency
24
12
� 10/29/2023
Central inverter
25
Central inverter
Advantages of a Disadvantages of a Central Inverter
Central Inverter oHigh DC wiring costs and power loss due to Voltage Drop.
oThe most traditional oSingle MPPT for the entire PV system
inverter topology oSystem output can be drastically reduced in case of partial
shading and string mismatch
oEasy system design
and implementation oDifficult to add strings or arrays for future expansion
oSingle failure point for the entire system
oLow cost per Watt
oMonitoring at array level
oEasy accessibility for
oHuge size! (It is a disadvantage because the bigger size
maintenance and
requires more land and creates a shading issue for the PV
troubleshooting array.)
26
13
� 10/29/2023
String inverter
27
String inverter
Advantages of a String Inverter
oSmaller in size when compared to central inverters
oBetter MPPT capability per string
oScalability for future expansion by adding parallel strings
oShort DC wires
oMonitoring at string level
Disadvantages of a String Inverter
oThe installation requires special racking for the inverter for each string
oPoor flexibility at partial shading
oHigher per Watt cost than central inverter
28
14
� 10/29/2023
Micro Inverter
29
Micro Inverter
Advantages of Micro Inverters
oResilience to partial shading effects as compared to the central and string inverters.
oMPPT at module level
oHighest system flexibility for future expansion
oMinimum DC wiring costs
oMonitoring at module level
Disadvantages of Micro Inverters
oHigh per Watt cost
oHigh maintenance costs
oDifficult access for maintenance since the installation is under the PV modules
30
15
� 10/29/2023
Example datasheet
31
Example datasheet
32
16
� 10/29/2023
Content
1. PV system architecture
2. PV system components
o Charge controller
o Inverter
o Battery
33
SOC and DOD
34
17
� 10/29/2023
Battery life
35
DOD vs Battery temperature
36
18
� 10/29/2023
Battery self discharge
37
Battery voltage
38
19
� 10/29/2023
Battery charging
Rated capacity
40
20
� 10/29/2023
Rated capacity
41
Connection in series/parallel
42
21