TVET colleges 2014
Develop and Use Complex Spreadsheets
Learning objectives
LO1:- Prepare to develop spreadsheet
LO2:- Develop a linked spreadsheet solution
LO3:-Automate and standardize spreadsheet operation
LO4:-Use spreadsheets
LO5:-Represent numerical data in graphic form
LO1:- Prepare to develop spreadsheet
Organize personal work environment in accordance with ergonomic requirements.
Analyze task and determine specifications for spreadsheets.
Identify organizational and task requirements in relation to data entry, storage, output, and reporting and
presentation requirements.
Apply work organization strategies and energy and resource conservation techniques to plan work
activities
Ergonomics
Ergonomic hazards occur when a caregiver’s nature of work, body position and working conditions put
pressure on his/her body. It is difficult to spot this type of hazard, because caregivers do not immediately
notice the effect to their bodies. At first, sore muscles may be experienced. But long term exposure to this
type of hazard can cause musculoskeletal problems.
Examples of ergonomic hazards that a caregiver may be exposed to:
Performing tasks that require lifting heavy loads,
Too much bending and reaching, standing for long periods of time,
Holding body parts for long period of time and awkward movements, especially if they are
repetitive,
Repeating the same movements over and over
Some of the Effects of Ergonomic Hazards: (pain in the shoulders, back injury, too much impact on
wrist and hands, numbness in some parts of the bodyand muscle cramps)
Ergonomic requirements may include
avoiding radiation from computer screens
chair height, seat and back adjustment
document holder
footrest
keyboard and mouse position
lighting
noise minimisation
posture
screen position
workstation height and layout
Work organization strategies may include:
exercise breaks
mix of repetitive and other activities
rest periods
Energy and resource conservation techniques may include:
By Abebe K. Page 1
�TVET colleges 2014
double-sided paper use
recycling used and shredded paper
re-using paper for rough drafts (observing confidentiality requirements)
using power-save options for equipment
LO2:- Develop a linked spreadsheet solution.
Utilize spreadsheet design software functions and formula to meet identified requirements
Link spreadsheets in accordance with software procedures
Format cells and use data attributes assigned with relative and/or absolute cell references, in accordance
with the task specifications
Test formula to confirm output meets task requirements
Spreadsheet design may include
analysis
appropriateness
avoidance of blank rows and columns
embedding cell references in formula
formula
formatting and reformatting
functions
headers and footers
headings
headings and labels
identification and parameters
import and export of data
labels
linked formula
multi-page documents
pivot tables
relative and absolute cell references
split screen operation
Formulas
A formula is a sequence of values, cell references, names, functions, or operators in a cell that together
produce a new value.
A formula always begins with an equal sign (=).And includes
Addition
Average
Comparison
division
exponentiation
multiplication
percentage
subtraction
combinations of above
By Abebe K. Page 2
�TVET colleges 2014
Functions may include
basic financial functions (if available)
date functions
logical functions (lookup, if, choose, true, false, conditions)
mathematical functions (square root, integer, absolute value, round)
simple nested functions
statistical functions (standard deviation, count, maximum, minimum)
Lo3:-Automate and standardize spreadsheet operation
Evaluate tasks to identify those where automation would increase efficiency
Create, use and edit macros to fulfill the requirements of the task and automate spreadsheet operation
Develop, edit and use templates to ensure consistency of design and layout for forms and reports, in
accordance with organizational requirements
Macros mean the process of printing sections of a spreadsheet.
Templates may include:
font types and sizes
forms
headers and footers
headings
page formats
reports
lo4:- Use spreadsheets
Enter, check and amend data in accordance with organizational and task requirements
Import and export data between compatible spreadsheets and adjust host documents, in accordance with
software and system procedures
Use manuals, user documentation and online help to overcome problems with spreadsheet design and
production
Preview, adjust and print spreadsheet in accordance with organizational and task requirements
Name and store spreadsheet in accordance with organizational requirements and exit the application
without data loss or damage
Importing and exporting datamay include:
proofreading
reformatting
split screen (if available)
Printingmay include:
charts
entire workbooks
selected data within a worksheet
worksheets
By Abebe K. Page 3
�TVET colleges 2014
Naming and storing spread sheets may include
o authorised access
o file naming conventions
o filing locations
o organizational policy for backing up files
o organizational policy for filing hard copies of spread sheets
o security
o storage in folders and sub-folders
o storage on disk drives, CD-ROM, USB, tape back-up, server
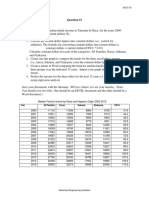
lo5:- Represent numerical data in graphic form
Determine style of graph to meet specified requirements and manipulate spreadsheet data if necessary to
suit graph requirements
Create graphs with labels and titles from numerical data contained in a spreadsheet file
Save, view and print graph within designated time lines
Graphs and create graphs includes
bar
line
pie
scatter
stack3D
data range
keys and legends
labels and titles
naming
sizing (if possible)
using graph menu
X and Y axis
By Abebe K. Page 4