0% found this document useful (0 votes)
87 views29 pagesNosql Databases Types
- Aggregation oriented databases store object aggregates rather than normalized tables, making data manipulation operations more efficient on distributed data. The query load dictates the database design.
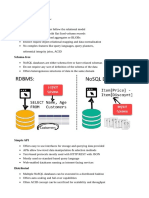
- The document discusses key-value stores, document databases, column family/wide column databases, and graph databases as types of NoSQL databases. Key-value stores use a dictionary/map concept to store key-value pairs, document databases add structure to values, and column family databases group columns into flexible column families.
- Document databases like MongoDB and CouchDB allow flexible or full schemas and support querying value attributes. Column family databases like HBase and Cassandra were inspired by BigTable and DynamoDB and support sparse, multidimensional data
Uploaded by
Parv AgarwalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
87 views29 pagesNosql Databases Types
- Aggregation oriented databases store object aggregates rather than normalized tables, making data manipulation operations more efficient on distributed data. The query load dictates the database design.
- The document discusses key-value stores, document databases, column family/wide column databases, and graph databases as types of NoSQL databases. Key-value stores use a dictionary/map concept to store key-value pairs, document databases add structure to values, and column family databases group columns into flexible column families.
- Document databases like MongoDB and CouchDB allow flexible or full schemas and support querying value attributes. Column family databases like HBase and Cassandra were inspired by BigTable and DynamoDB and support sparse, multidimensional data
Uploaded by
Parv AgarwalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 29