0% found this document useful (0 votes)
110 views29 pagesCube Implementations
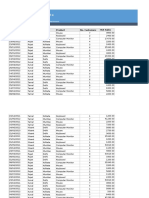
The document discusses data cube implementation and OLAP systems. A data cube is represented as a lattice of cuboids, where each node is a cuboid containing aggregated measures for a dimension combination. Cuboids allow for drill down and roll up queries. Relational and multidimensional OLAP systems are discussed for storing and querying the cube lattice. Relational OLAP stores cuboids in tables while multidimensional OLAP stores them as multi-dimensional arrays. Large scale OLAP systems like Apache Kylin, Druid, and Presto are also mentioned.
Uploaded by
Parv AgarwalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
110 views29 pagesCube Implementations
The document discusses data cube implementation and OLAP systems. A data cube is represented as a lattice of cuboids, where each node is a cuboid containing aggregated measures for a dimension combination. Cuboids allow for drill down and roll up queries. Relational and multidimensional OLAP systems are discussed for storing and querying the cube lattice. Relational OLAP stores cuboids in tables while multidimensional OLAP stores them as multi-dimensional arrays. Large scale OLAP systems like Apache Kylin, Druid, and Presto are also mentioned.
Uploaded by
Parv AgarwalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 29