0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views7 pagesSecurity
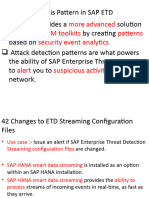
The document discusses the RFC interface in SAP systems which enables function calls between two SAP systems or between an SAP system and an external system. It describes the calling interface for ABAP programs and interfaces for calling non-ABAP programs. It also provides details on writing and calling RFC function modules in ABAP.
Uploaded by
AndreaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views7 pagesSecurity
The document discusses the RFC interface in SAP systems which enables function calls between two SAP systems or between an SAP system and an external system. It describes the calling interface for ABAP programs and interfaces for calling non-ABAP programs. It also provides details on writing and calling RFC function modules in ABAP.
Uploaded by
AndreaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 7