0% found this document useful (0 votes)
595 views7 pagesSelection Structure
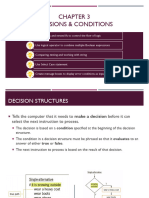
The document discusses selection structures in programming which allow a program to choose between multiple paths of execution based on conditions. It covers if/then/else statements, logical and relational operators, nested selection structures, and the case/select structure.
Uploaded by
Suja MaryCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
595 views7 pagesSelection Structure
The document discusses selection structures in programming which allow a program to choose between multiple paths of execution based on conditions. It covers if/then/else statements, logical and relational operators, nested selection structures, and the case/select structure.
Uploaded by
Suja MaryCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 7