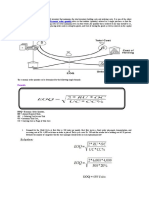
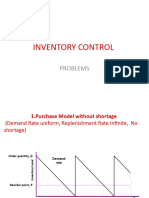
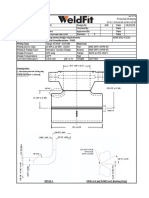
1.
The following information is available in respect of material A :
Maximum usage -300 units
Minimum usage – 200 units
Normal usage – 225 units
Time lag in procurement of material – Maximum 6 months, Minimum 2 months.
Reorder quantiy – 750 units
Calculate :
(a) Re-order level
(b) Minimum level
(c) Maximum level
(d) Average level
2. Kuber manufacturing company estimates that its carrying cost is 15% and its ordering cost is
Rs.9 per order. The estimated annual requirement is 48000 units at a price of Rs. 4 per unit.
Based on information provided respond to the following questions
(i) What is the most economical number of units to order?
(ii) How many orders should be placed in a year?
(iii) How often should an order be placed?
3. The following particulars about a product are available:
Normal usage (per week) = 60 nos.
Maximum usage (per week) = 80 nos.
Minimum usage (per week) = 30 nos.
Reorder quantity 400 nos.
Reorder period 4 to 6 weeks.
Based on the above information, you are required to calculate:
(a) Reorder level
(b) Minimum level
(c) Maximum level
(d) Average level
4. PQR Limited produced a product which has monthly demand of 52000 units. The product
requires a component X which is purchased at ₹ 15 per unit. For every finished product, 2
units of component X are required. The ordering cost is ₹ 350 per order and the carrying cost
is 12% p.a., You are required to:
(a) Calculate the Economic order quantity for component X
(b) Total number of orders to be placed in a year as per EOQ.
(c) Time between two orders in the number of days.
5. G Limited produced a product which has monthly demand of 4000 units. The product
requires a component X which is purchased at ₹ 20 per unit. For every finished product, one
unit of component X is required. The ordering cost is ₹ 120 per order and the holding cost is
10% p.a., You are required to:
(d) Economic order quantity (EOQ)
(e) No. of orders
(f) Time between orders in the number of days.
�6. A Ltd. provides the following information in respect of Material X.
Supply period: 5 to 15 days
Rate of consumption:
Average: 15 units per day
Maximum: 20 units per day
Yearly requirement is 5,000 units
Ordering cost: Rs. 20 per order
Purchase price per unit: Rs. 50
Storage cost : 10% of unit value
1. Compute a) Re-order Level b) Maximum Level
7. Atul Manufacturing Company estimates its carrying cost at 15% and its ordering cost is Rs. 9
per order. The estimated annual requirement is 48,000 units at a price of Rs. 4 per unit.
Based on information provided respond to the following questions.
i. What is the most economical number of units to order?
ii. How many orders should be placed in a year?
iii. How often should an order be placed?
8. The annual demand for a product is 6400 units. The unit cost is ₹6 and inventory carrying
cost per unit per annum is 25% of the average inventory cost. If the cost of procurement is ₹
75. Calculate:
(a) Economic order Quantity
(b) Number of orders per annum
(c) Time between two consecutive orders.
9. For the manufacture of a product X, two components A and B are used. The following
particulars about the components are
Normal usage (per week) 300 nos
Maximum usage (per week) 450 nos.
Minimum usage (per week) 150 nos.
Reorder Quantity A – 2400 nos, B – 3600 nos.
Reorder period A- 4 to 6 weeks, B- 2 to 4 weeks.
You are required to calculate the following for both the components.
(a) Reorder Quantity
(b) Maximum level and
(c) Minimum level.