0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views15 pagesSSAD Practicals
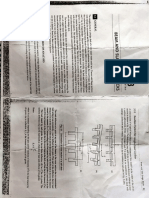
The document describes a student information management system (SIMS) that tracks student records and generates reports. It outlines the system's modules for functions like login, student information, administration, and more. It also provides details on developing a software requirements specification and conducting a feasibility study for the technical, economic, legal, operational, and scheduling aspects.
Uploaded by
sksinghirbn0Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views15 pagesSSAD Practicals
The document describes a student information management system (SIMS) that tracks student records and generates reports. It outlines the system's modules for functions like login, student information, administration, and more. It also provides details on developing a software requirements specification and conducting a feasibility study for the technical, economic, legal, operational, and scheduling aspects.
Uploaded by
sksinghirbn0Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 15