0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views5 pagesSurvey Assignment
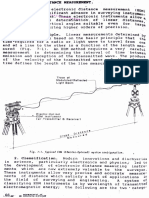
A compound curve is a combination of two or more circular curves that meet at a common point of compound curvature. A reverse curve is a combination of two simple curves with opposite directions joining at a common tangent point. The summary distinguishes between passive and active EDMs, carrier and modulation signals, retro-reflectors and remotes, known and unknown baselines, modular and integrated EDMs, and mid-ordinate and apex distances.
Uploaded by
StephanieCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views5 pagesSurvey Assignment
A compound curve is a combination of two or more circular curves that meet at a common point of compound curvature. A reverse curve is a combination of two simple curves with opposite directions joining at a common tangent point. The summary distinguishes between passive and active EDMs, carrier and modulation signals, retro-reflectors and remotes, known and unknown baselines, modular and integrated EDMs, and mid-ordinate and apex distances.
Uploaded by
StephanieCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5