0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views6 pagesComputer Science Unit-2 - 2 Sem1
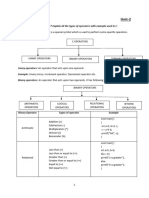
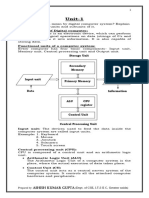
The document discusses different types of conditional statements in programming including if, if else, if else if else, and switch case statements. Syntax and examples are provided for each type of conditional statement.
Uploaded by
aditya67857Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views6 pagesComputer Science Unit-2 - 2 Sem1
The document discusses different types of conditional statements in programming including if, if else, if else if else, and switch case statements. Syntax and examples are provided for each type of conditional statement.
Uploaded by
aditya67857Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6