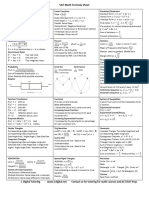
SAT Math Formula Sheet
Rules of Exponents Linear Functions Parabolas/Quadratics
𝑥𝑚 𝑦 −𝑦
𝑥 𝑚 ∙ 𝑥 𝑛 = 𝑥 𝑚+𝑛 = 𝑥 𝑚−𝑛 Slope = 2 1 Standard Form: 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐
𝑥𝑛 𝑥2 −𝑥1
Vertex Form: 𝑦 = 𝑎(𝑥 − ℎ)2 + 𝑘
(𝑥 𝑚 )𝑛 = 𝑥 𝑚𝑛 𝑥0 = 1 Slope-Intercept Form: 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑏
𝑎
𝑏 1 1 Parallel: Same Slope Intercept Form: 𝑦 = 𝑎(𝑥 − 𝑝)(𝑥 − 𝑞)
𝑥 𝑏 = √𝑥 𝑎 𝑥 −1 = =𝑥 𝑏 𝑏
2𝑥 𝑥+4
𝑥 𝑥 −1 Perpendicular: Negative Reciprocal Find vertex: ℎ = − 𝑘 = 𝑓 (− )
4 =8 change to same base. Set exponents 2𝑎 2𝑎
System of: Substitution or Elimination method If a positive, it’s upward otherwise downward
equal to each other and solve 𝑏
Y-Intercept: Occurs at x=0 Sum of solutions = −
𝑎
X-Intercept: Occurs at y=0
Quadratic Formula Percent Statistics
𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑡 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑝 𝑠𝑢𝑚
−𝑏 ± √𝑏 2 − 4𝑎𝑐 = p% of x = (𝑥) Mean =
𝑐𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑡
𝑥= 𝑤ℎ𝑜𝑙𝑒 100 100
∑ 𝑓∙𝑥
2𝑎 1.3p is p increased by 30% Mean of Frequency Distribution
Discriminant Rules 0.7p is p decreased by 30%
∑𝑓
𝑏 2 − 4𝑎𝑐 > 0 Two real roots Median: Least to greatest. Middle term
Absolute value Equation
𝑏 2 − 4𝑎𝑐 = 0 One real root |𝑥 + 5| = 3 Margin of Error: 𝑧√
𝜎2
𝑏 2 − 4𝑎𝑐 < 0 Two imaginary roots 𝑥 + 5 = 3 𝑥 + 5 = −3
𝑛
Range: Highest minus lowest
Standard Deviation: Measure of variation
Probability Circle Arc Circle Sector Imaginary Numbers
𝐹𝑎𝑣𝑜𝑟𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒 𝑂𝑢𝑡𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑒𝑠 𝑥 𝑥
𝑃(𝐴) = ∙ Circumference ∙ Area 𝑖 = √−1 𝑖 2 = −1
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑃𝑜𝑠𝑠𝑖𝑏𝑙𝑒 𝑂𝑢𝑡𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑒𝑠 360 360
𝑃(𝐴 𝑜𝑟 𝐵) = 𝑃(𝐴) + 𝑃(𝐵) − 𝑃(𝐴 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝐵) where x = Central Angle Interpreting Linear Equations
𝑃(𝐴 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝐵) = 𝑃(𝐴) ∙ 𝑃(𝐵) Slope value: For every 1 increase of x, y
Sum of Probability Distribution = 1 increases by the slope value
Given: Reduces total possible outcomes Y-Intercept: The initial value
Boxplot Interpreting Exponential Equations
Initial Value: 𝐴0 Growth Factor: 1 + 𝑟
Growth Percent: 𝑟 ∗ 100
𝑡
Growth factor of 1.25 every 5 days: (1.25)5
Function Translations Functions System of Inequalities
𝑓(𝑥) + 𝑐 shift up 𝑓(3) set x=3 and evaluate A point must work in all the inequalities to be
𝑓(𝑥) − 𝑐 shift down Zeros of Functions a solution
𝑓(𝑥 + 𝑐) shift left x values that cause the y value to be zero Exponential Functions
𝑓(𝑥 − 𝑐) shift right Vertical Asymptote 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑎𝑏 𝑥
−𝑓(𝑥) reflection about x axis Located at x values that cause division by zero Exponential Growth/Decay
𝑓(−𝑥) reflection about y axis Increasing Linear Function 𝐴 = 𝐴0 (1 + 𝑟)𝑡 𝐴 = 𝐴0 (1 − 𝑟)𝑡
𝑡
Projectile Motion Y-Increases by the same amount for each 𝐴 = 𝐴0 (1 + 𝑟)𝑚
ℎ(𝑥) = −16(𝑥 − ℎ)2 + 𝑘 feet increment of X.
Increasing Exponential Function
ℎ(𝑥) = −4.9(𝑥 − ℎ)2 + 𝑘 meters
Y increased by the same factor or percentage
for each increment of X.
Similar Triangles Trig Identities Geometry
Corresponding angles congruent sin (𝜃) Isosceles Triangle: Two sides congruent and
tan (𝜃) = sin(𝜃) = 𝑐𝑜𝑠 (90 − 𝜃)
cos (𝜃)
Corresponding sides proportional corresponding angles congruent
cos(𝜃) = 𝑠𝑖𝑛 (90 − 𝜃)
Side-Angle-Side | Angle-Angle | Side-Side-Side Pythagorean Theorem: 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 = 𝑐 2
Scatter Plot
Congruent Triangles Pythagorean Triplets: 3-4-5, 6-8-10, 5-12-13
Points above the line – Best fit line
Corresponding sides and angles congruent Triangle: Interior angles sum is 180
underestimated.
Side-Side-Side | Side-Angle-Side | Angle-Side-
Points below the line – Best fir lint
angle | Angle-Angle-Side | Hypotenuse-Side
overestimated
SOHCAHTOA Special Right Triangles Perimeter
𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 Circle: 2𝜋𝑟 = 𝜋𝑑
𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑒 = 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑒 = 30-60-90: 𝑥, 𝑥√3, 2𝑥
ℎ𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 ℎ𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒
𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 45-45-90: 𝑥, 𝑥, 𝑥√2 Area
𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒𝑛𝑡 = 1
𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 Circle: (𝑥 − ℎ)2 + (𝑦 − 𝑘)2 = 𝑟 2 Rectangle: L x W Triangle: 𝑏ℎ
2
System of Linear Equations Use completing to square to convert to circle 1
Circle: 𝜋𝑟 2 Trapezoid: ℎ(𝑏1 + 𝑏2 )
One Solution: Difference Slopes equation 2
Multiple Solutions: Same slope and y-intercept 𝑀𝑎𝑠𝑠 Volume
Density: Rect Prism: 𝐿𝑥𝑊𝑥𝐻
No Solutions: Same slope different y-intercepts 𝑉𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒
J. Digital Tutoring www.j-digital.net Contact us for tutoring for math courses and ACT/SAT Prep
�Website
www.j-digital.net
Email
jdigital7850@gmail.com
Facebook Group
SAT Exam Prep & Discussion
https://www.facebook.com/groups/824379568968364
Prep Opportunities
One-on-One Tutoring
SAT Math Prep Course