Contents
1 Program 01 2
1.1 Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
2 Program 02 4
2.1 Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
3 Program 03 6
3.1 Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
4 Program 04 9
4.1 Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
5 Program 05 12
5.1 Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
6 Program 06 15
6.1 Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
7 Program 07 17
7.1 Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
8 Program 08 18
8.1 Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
9 Program 09 20
9.1 Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
10 Program 10 21
10.1 Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
11 Program 11 22
11.1 Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
12 Program 12 23
12.1 Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1
�1 Program 01
Develop a program to draw a line using Bresenham’s line drawing technique.
1.1 Code
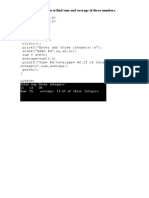
import turtle
def bresenham_line ( x1 , y1 , x2 , y2 ) :
# Calculate the deltas
dx = abs ( x2 - x1 )
dy = abs ( y2 - y1 )
# Determine the step direction for each axis
x_step = 1 if x1 < x2 else -1
y_step = 1 if y1 < y2 else -1
# Initialize the error term
error = 2 * dy - dx
# Initialize the line points
line_points = []
# Start at the first point
x , y = x1 , y1
# Draw the line
for _ in range ( dx + 1) :
# Add the current point to the line
line_points . append (( x , y ) )
# Update the error term and adjust the
coordinates
if error > 0:
y += y_step
error -= 2 * dx
error += 2 * dy
x += x_step
return line_points
# Example usage
turtle . setup (500 , 500)
turtle . speed (0) # Fastest drawing speed
2
�x1 , y1 = 100 , 100
x2 , y2 = 400 , 300
line_points = bresenham_line ( x1 , y1 , x2 , y2 )
# Draw the line
turtle . penup ()
turtle . goto ( x1 , y1 )
turtle . pendown ()
for x , y in line_points :
turtle . goto (x , y )
turtle . exitonclick ()
Listing 1: Bresenham’s Line Drawing Algorithm
3
�2 Program 02
Develop a program to demonstrate basic geometric operations on the 2D object.
2.1 Code
import turtle
import math
# Set up the screen
screen = turtle . Screen ()
screen . title ( " Geometric ␣ Transformations ␣ with ␣ Turtle " )
screen . bgcolor ( " white " )
# Create a turtle to draw the original square
t = turtle . Turtle ()
def draw_square (t , vertices , color ) :
t . penup ()
t . goto ( vertices [0])
t . pendown ()
t . color ( color )
for vertex in vertices [1:]:
t . goto ( vertex )
t . goto ( vertices [0])
def translate ( vertices , tx , ty ) :
return [( x + tx , y + ty ) for x , y in vertices ]
def rotate ( vertices , angle ) :
theta = math . radians ( angle )
return [( x * math . cos ( theta ) - y * math . sin ( theta ) ,
x * math . sin ( theta ) + y * math . cos ( theta ) ) for
x , y in vertices ]
def scale ( vertices , sx , sy ) :
return [( x * sx , y * sy ) for x , y in vertices ]
# Define the original square vertices
square_vertices = [(50 , 50) , (150 , 50) , (150 , 150) ,
(50 , 150) ]
# Draw the original square
draw_square (t , square_vertices , " black " )
4
�# Translate the square
t r an s l at e d _v e r ti c e s = translate ( square_vertices , 200 ,
100)
draw_square (t , translated_vertices , " blue " )
# Rotate the square
rotated_vertices = rotate ( square_vertices , 45)
draw_square (t , rotated_vertices , " red " )
# Scale the square
scaled_vertices = scale ( square_vertices , 0.5 , 0.5)
draw_square (t , scaled_vertices , " green " )
# Hide the turtle and display the window
t . hideturtle ()
turtle . done ()
Listing 2: Basic Geometric Operations on the 2D Object
5
�3 Program 03
Develop a program to demonstrate basic geometric operations on the 3D object.
3.1 Code
import numpy as np
import matplotlib . pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits . mplot3d . art3d import
Poly3DCollection
# Define the cube vertices
def create_cube () :
vertices = np . array ([
[0 , 0 , 0] ,
[1 , 0 , 0] ,
[1 , 1 , 0] ,
[0 , 1 , 0] ,
[0 , 0 , 1] ,
[1 , 0 , 1] ,
[1 , 1 , 1] ,
[0 , 1 , 1]
])
return vertices
# Define the faces of the cube
def create_faces ( vertices ) :
faces = [
[ vertices [ j ] for j in [0 , 1, 2, 3]] ,
[ vertices [ j ] for j in [4 , 5, 6, 7]] ,
[ vertices [ j ] for j in [0 , 1, 5, 4]] ,
[ vertices [ j ] for j in [2 , 3, 7, 6]] ,
[ vertices [ j ] for j in [1 , 2, 6, 5]] ,
[ vertices [ j ] for j in [4 , 7, 3, 0]]
]
return faces
# Translation function
def translate ( vertices , tx , ty , tz ) :
tr an sl at io n_ ma tr ix = np . array ([ tx , ty , tz ])
return vertices + tra ns la ti on _m at ri x
# Rotation function ( around the Z axis )
def rotate ( vertices , angle ) :
theta = np . radians ( angle )
6
� rotation_matrix = np . array ([
[ np . cos ( theta ) , - np . sin ( theta ) , 0] ,
[ np . sin ( theta ) , np . cos ( theta ) , 0] ,
[0 , 0 , 1]
])
return np . dot ( vertices , rotation_matrix )
# Scaling function
def scale ( vertices , sx , sy , sz ) :
scaling_matrix = np . array ([
[ sx , 0 , 0] ,
[0 , sy , 0] ,
[0 , 0 , sz ]
])
return np . dot ( vertices , scaling_matrix )
# Plotting function
def plot_cube ( vertices , title ) :
fig = plt . figure ()
ax = fig . add_subplot (111 , projection = ’3 d ’)
faces = create_faces ( vertices )
face_collection = Poly3DCollection ( faces , alpha
=0.25 , linewidths =1 , edgecolors = ’r ’)
face_collection . set_facecolor ( ’ cyan ’)
ax . add_collection3d ( face_collection )
# Plot the vertices
ax . scatter3D ( vertices [: , 0] , vertices [: , 1] ,
vertices [: , 2])
# Setting the plot title
ax . set_title ( title )
# Set labels
ax . set_xlabel ( ’X ’)
ax . set_ylabel ( ’Y ’)
ax . set_zlabel ( ’Z ’)
# Set the aspect ratio to be equal
ax . set_box_aspect ([1 ,1 ,1])
plt . show ()
# Create the original cube
original_cube = create_cube ()
7
�# Plot the original cube
plot_cube ( original_cube , " Original ␣ Cube " )
# Translate the cube
translated_cube = translate ( original_cube , 2 , 3 , 1)
plot_cube ( translated_cube , " Translated ␣ Cube ␣ ( tx =2 , ␣ ty
=3 , ␣ tz =1) " )
# Rotate the cube
rotated_cube = rotate ( original_cube , 45)
plot_cube ( rotated_cube , " Rotated ␣ Cube ␣ (45 ␣ degrees ␣
around ␣Z - axis ) " )
# Scale the cube
scaled_cube = scale ( original_cube , 1.5 , 0.5 , 2)
plot_cube ( scaled_cube , " Scaled ␣ Cube ␣ ( sx =1.5 , ␣ sy =0.5 , ␣
sz =2) " )
Listing 3: Basic Geometric Operations on the 3D Object
8
�4 Program 04
Develop a program to demonstrate 2D transformation on basic objects.
4.1 Code
import matplotlib . pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def plot_shape ( vertices , color = ’b ’ , label = None ) :
vertices = np . append ( vertices , [ vertices [0]] , axis
=0) # Close the shape
plt . plot ( vertices [: , 0] , vertices [: , 1] , color =
color , label = label )
def translate ( vertices , tx , ty ) :
tr an sl at io n_ ma tr ix = np . array ([[1 , 0 , tx ] ,
[0 , 1 , ty ] ,
[0 , 0 , 1]])
v e r t i c e s _ h o m o g e n e o u s = np . hstack ([ vertices , np . ones
(( vertices . shape [0] , 1) ) ])
t ra n s la t e d_ v e rt i c es = v e r t i c e s _ h o m o g e n e o u s . dot (
tr an sl at io n_ ma tr ix . T )
return t ra n s la t e d_ v e rt i c es [: , :2]
def rotate ( vertices , angle ) :
theta = np . radians ( angle )
rotation_matrix = np . array ([[ np . cos ( theta ) , - np . sin
( theta ) , 0] ,
[ np . sin ( theta ) , np . cos
( theta ) , 0] ,
[0 , 0 , 1]])
v e r t i c e s _ h o m o g e n e o u s = np . hstack ([ vertices , np . ones
(( vertices . shape [0] , 1) ) ])
rotated_vertices = v e r t i c e s _ h o m o g e n e o u s . dot (
rotation_matrix . T )
return rotated_vertices [: , :2]
def scale ( vertices , sx , sy ) :
scaling_matrix = np . array ([[ sx , 0 , 0] ,
[0 , sy , 0] ,
[0 , 0 , 1]])
v e r t i c e s _ h o m o g e n e o u s = np . hstack ([ vertices , np . ones
(( vertices . shape [0] , 1) ) ])
9
� scaled_vertices = v e r t i c e s _ h o m o g e n e o u s . dot (
scaling_matrix . T )
return scaled_vertices [: , :2]
def main () :
# Define the original square vertices
square_vertices = np . array ([
[1 , 1] ,
[3 , 1] ,
[3 , 3] ,
[1 , 3]
])
# Define the original triangle vertices
tria ngle_v ertice s = np . array ([
[4 , 1] ,
[5 , 3] ,
[6 , 1]
])
plt . figure ()
plt . axis ( ’ equal ’)
plt . grid ( True )
# Plot the original square and triangle
plot_shape ( square_vertices , color = ’b ’ , label = ’
Original ␣ Square ’)
plot_shape ( triangle_vertices , color = ’c ’ , label = ’
Original ␣ Triangle ’)
# Apply and plot the translated square and triangle
tran slated _squar e = translate ( square_vertices , 2 ,
2)
plot_shape ( translated_square , color = ’r ’ , label = ’
Translated ␣ Square ␣ ( tx =2 , ␣ ty =2) ’)
t ra n s la t e d_ t r ia n g le = translate ( triangle_vertices ,
2 , 2)
plot_shape ( translated_triangle , color = ’m ’ , label = ’
Translated ␣ Triangle ␣ ( tx =2 , ␣ ty =2) ’)
# Apply and plot the rotated square and triangle
rotated_square = rotate ( square_vertices , 45)
plot_shape ( rotated_square , color = ’g ’ , label = ’
Rotated ␣ Square ␣ (45 ␣ degrees ) ’)
10
� rotated_triangle = rotate ( triangle_vertices , 45)
plot_shape ( rotated_triangle , color = ’y ’ , label = ’
Rotated ␣ Triangle ␣ (45 ␣ degrees ) ’)
# Apply and plot the scaled square and triangle
scaled_square = scale ( square_vertices , 1.5 , 0.5)
plot_shape ( scaled_square , color = ’ purple ’ , label = ’
Scaled ␣ Square ␣ ( sx =1.5 , ␣ sy =0.5) ’)
scaled_triangle = scale ( triangle_vertices , 1.5 ,
0.5)
plot_shape ( scaled_triangle , color = ’ orange ’ , label = ’
Scaled ␣ Triangle ␣ ( sx =1.5 , ␣ sy =0.5) ’)
plt . legend ()
plt . title ( ’2 D ␣ Transformations ␣ on ␣ a ␣ Square ␣ and ␣ a ␣
Triangle ’)
plt . xlabel ( ’X - axis ’)
plt . ylabel ( ’Y - axis ’)
plt . show ()
if __name__ == " __main__ " :
main ()
Listing 4: 2D Transformation on Basic Objects
11
�5 Program 05
Develop a program to demonstrate 3D transformation on 3D objects.
5.1 Code
import pygame
from pygame . locals import *
from OpenGL . GL import *
from OpenGL . GLU import *
import numpy as np
# Define vertices , edges , and colors of a proper cube
vertices = ((1 , -1 , -1) ,(1 ,1 , -1) ,( -1 ,1 , -1) ,( -1 , -1 , -1)
,(1 , -1 ,1) ,(1 ,1 ,1) ,( -1 , -1 ,1) ,( -1 ,1 ,1) )
edges = ((0 , 1) ,(1 , 2) ,(2 , 3) ,(3 , 0) ,(4 , 5) ,(5 , 6) ,(6 ,
7) ,(7 , 4) ,(0 , 4) ,(1 , 5) ,(2 , 6) ,(3 , 7) )
surfaces = ((0 , 1 , 2 , 3) ,(3 , 2 , 7 , 6) ,(6 , 7 , 5 , 4) ,(4 ,
5 , 1 , 0) ,(1 , 5 , 7 , 2) ,(4 , 0 , 3 , 6) )
colors = ((1 , 0 , 0) ,(0 , 1 , 0) ,(0 , 0 , 1) ,(1 , 1 , 0) ,(1 ,
0 , 1) ,(0 , 1 , 1) ,(1 , 1 , 1) ,(0.5 , 0.5 , 0.5) )
def draw_cube () :
glBegin ( GL_QUADS )
for surface in surfaces :
for vertex in surface :
glColor3fv ( colors [ vertex ])
glVertex3fv ( vertices [ vertex ])
glEnd ()
glBegin ( GL_LINES )
for edge in edges :
for vertex in edge :
glColor3fv ((0 , 0 , 0) )
glVertex3fv ( vertices [ vertex ])
glEnd ()
def main () :
pygame . init ()
display = (800 , 600)
pygame . display . set_mode ( display , DOUBLEBUF | OPENGL
)
12
�gluPerspective (45 , ( display [0] / display [1]) , 0.1 ,
50.0)
glTranslatef (0.0 , 0.0 , -5)
# Variables for transformations
angle_x = 0
angle_y = 0
scale = 1.0
x_translation = 0
y_translation = 0
clock = pygame . time . Clock ()
while True :
for event in pygame . event . get () :
if event . type == pygame . QUIT :
pygame . quit ()
return
elif event . type == KEYDOWN :
if event . key == K_LEFT :
angle_y -= 5
elif event . key == K_RIGHT :
angle_y += 5
elif event . key == K_UP :
angle_x -= 5
elif event . key == K_DOWN :
angle_x += 5
elif event . key == K_PLUS or event . key
== K_EQUALS :
scale += 0.1
elif event . key == K_MINUS or event . key
== K_UNDERSCORE :
scale -= 0.1
# Clear the screen and set the color
glClear ( G L_ C O LO R _ BU F F ER _ B IT |
G L_ D E PT H _ BU F F ER _ B I T )
glClearColor (0.0 , 0.0 , 0.0 , 1.0)
# Apply transformations
glPushMatrix ()
glTranslatef ( x_translation , y_translation , 0)
glRotatef ( angle_x , 1 , 0 , 0)
glRotatef ( angle_y , 0 , 1 , 0)
glScalef ( scale , scale , scale )
13
� # Draw the cube
draw_cube ()
glPopMatrix ()
pygame . display . flip ()
clock . tick (60)
if __name__ == " __main__ " :
main ()
Listing 5: 3D Transformation on 3D Objects
14
�6 Program 06
Develop a program to demonstrate Animation effects on simple objects.
6.1 Code
import pygame
from pygame . locals import *
from OpenGL . GL import *
from OpenGL . GLU import *
import math
import numpy as np
# Function to draw a circle
def draw_circle ( radius , num_segments ) :
glBegin ( GL_TRIANGLE_FAN )
for i in range ( num_segments + 1) :
angle = 2.0 * math . pi * i / num_segments
x = radius * math . cos ( angle )
y = radius * math . sin ( angle )
glVertex2f (x , y )
glEnd ()
def main () :
pygame . init ()
display = (800 , 600)
pygame . display . set_mode ( display , DOUBLEBUF | OPENGL
)
gluOrtho2D ( -400 , 400 , -300 , 300)
# Variables for animations
angle = 0
scale = 1.0
x_translation = 0
y_translation = 0
color_change = 0
clock = pygame . time . Clock ()
while True :
for event in pygame . event . get () :
if event . type == pygame . QUIT :
pygame . quit ()
return
15
� # Clear the screen and set the color
glClear ( G L_ C O LO R _ BU F F ER _ B IT )
glClearColor (0.0 , 0.0 , 0.0 , 1.0)
# Apply transformations
glPushMatrix ()
glTranslatef ( x_translation , y_translation , 0)
glRotatef ( angle , 0 , 0 , 1)
glScalef ( scale , scale , 1.0)
# Apply color change
red = 0.5 * (1 + np . sin ( color_change ) )
green = 0.5 * (1 + np . cos ( color_change ) )
blue = 0.5 * (1 - np . sin ( color_change ) )
glColor3f ( red , green , blue )
# Draw the circle
draw_circle (100 , 50)
glPopMatrix ()
# Update animations
angle += 1 # Rotate
scale = 1.5 + 0.5 * np . sin ( pygame . time .
get_ticks () * 0.001) # Scale with time
x_translation = 200 * np . sin ( pygame . time .
get_ticks () * 0.001) # Translate with time
y_translation = 150 * np . cos ( pygame . time .
get_ticks () * 0.001) # Translate with time
color_change += 0.01 # Change color over time
pygame . display . flip ()
clock . tick (60)
if __name__ == " __main__ " :
main ()
Listing 6: Animation Effects on Simple Objects
16
�7 Program 07
Write a Program to read a digital image. Split and display image into 4 quad-
rants, up, down, right and left.
7.1 Code
import cv2
# Load the image
image = cv2 . imread ( " C :/ Desktop ␣ Folders / flower . jpg " )
# Check if the image was successfully loaded
if image is None :
print ( " Error : ␣ Could ␣ not ␣ load ␣ image . " )
exit ()
# Get the dimensions of the image
height , width , _ = image . shape
# Calculate the center points
center_y , center_x = height // 2 , width // 2
# Split the image into 4 quadrants
upper_left = image [: center_y , : center_x ]
upper_right = image [: center_y , center_x :]
lower_left = image [ center_y : , : center_x ]
lower_right = image [ center_y : , center_x :]
# Display the quadrants
cv2 . imshow ( ’ Upper ␣ Left ’ , upper_left )
cv2 . imshow ( ’ Upper ␣ Right ’ , upper_right )
cv2 . imshow ( ’ Lower ␣ Left ’ , lower_left )
cv2 . imshow ( ’ Lower ␣ Right ’ , lower_right )
# Wait for a key press and close all windows
cv2 . waitKey (0)
cv2 . d estroy AllWin dows ()
Listing 7: Split and display image into 4 quadrants
17
�8 Program 08
Write a program to show rotation, scaling, and translation on an image.
8.1 Code
import cv2
import numpy as np
# Load the image
image = cv2 . imread ( " C :/ Desktop ␣ Folders / flower . jpg " )
# Check if the image was successfully loaded
if image is None :
print ( " Error : ␣ Could ␣ not ␣ load ␣ image . " )
exit ()
# Get the dimensions of the image
height , width = image . shape [:2]
# Function to show the image in a window
def show_image ( window_name , img ) :
cv2 . imshow ( window_name , img )
cv2 . waitKey (0)
cv2 . d estroy AllWin dows ()
# 1. Rotation
# Define the center of rotation and the rotation angle
center = ( width // 2 , height // 2)
angle = 45 # Rotate by 45 degrees
scale = 1.0 # No scaling
# Get the rotation matrix
rotation_matrix = cv2 . g e t Ro t a ti o n Ma t r ix 2 D ( center ,
angle , scale )
# Perform the rotation
rotated_image = cv2 . warpAffine ( image , rotation_matrix ,
( width , height ) )
show_image ( ’ Rotated ␣ Image ’ , rotated_image )
# 2. Scaling
# Define the scaling factors
scale_x , scale_y = 0.5 , 0.5 # Scale to half the
original size
# Perform the scaling
18
�scaled_image = cv2 . resize ( image , None , fx = scale_x , fy =
scale_y , interpolation = cv2 . INTER_LINEAR )
show_image ( ’ Scaled ␣ Image ’ , scaled_image )
# 3. Translation
# Define the translation matrix
tx , ty = 100 , 50 # Translate by 100 pixels in x and
50 pixels in y
t ran sl at io n_ ma tr ix = np . float32 ([[1 , 0 , tx ] , [0 , 1 , ty
]])
# Perform the translation
translated_image = cv2 . warpAffine ( image ,
translation_matrix , ( width , height ) )
show_image ( ’ Translated ␣ Image ’ , translated_image )
Listing 8: Rotation, Scaling, and Translation on an Image
19
�9 Program 09
Read an image and extract and display low-level features such as edges, textures
using filtering techniques.
9.1 Code
import cv2
import numpy as np
# Load the image
image_path = ’C :/ Desktop ␣ Folders / rose . jpg ’ # Replace
with the path to your image
img = cv2 . imread ( image_path )
# Convert the image to grayscale
gray = cv2 . cvtColor ( img , cv2 . COLOR_BGR2GRAY )
# Edge detection
edges = cv2 . Canny ( gray , 100 , 200) # Use Canny edge
detector
# Texture extraction
kernel = np . ones ((5 , 5) , np . float32 ) / 25 # Define a 5
x5 averaging kernel
texture = cv2 . filter2D ( gray , -1 , kernel ) # Apply the
averaging filter for texture extraction
# Display the original image , edges , and texture
cv2 . imshow ( " Original ␣ Image " , img )
cv2 . imshow ( " Edges " , edges )
cv2 . imshow ( " Texture " , texture )
Listing 9: Display Features such as edges, textures
20
�10 Program 10
Write a program to blur and smoothing an image.
10.1 Code
import cv2
# Load the image
image = cv2 . imread ( ’C :/ Desktop ␣ Folders / rose . jpg ’)
# Gaussian Blur
gaussian_blur = cv2 . GaussianBlur ( image , (5 , 5) , 0)
# Median Blur
median_blur = cv2 . medianBlur ( image , 5)
# Bilateral Filter
bilateral_filter = cv2 . bilateralFilter ( image , 9 , 75 ,
75)
# Display the original and processed images
cv2 . imshow ( ’ Original ␣ Image ’ , image )
cv2 . imshow ( ’ Gaussian ␣ Blur ’ , gaussian_blur )
cv2 . imshow ( ’ Median ␣ Blur ’ , median_blur )
cv2 . imshow ( ’ Bilateral ␣ Filter ’ , bilateral_filter )
# Wait for a key press to close the windows
cv2 . waitKey (0)
cv2 . d estroy AllWin dows ()
Listing 10: Blur and Smoothing an Image
21
�11 Program 11
Write a program to contour an image.
11.1 Code
import cv2
import numpy as np
# Load the image
image = cv2 . imread ( ’C :/ Desktop ␣ Folders / flower . jpg ’)
# Convert the image to grayscale
gray = cv2 . cvtColor ( image , cv2 . COLOR_BGR2GRAY )
# Apply binary thresholding
ret , thresh = cv2 . threshold ( gray , 0 , 255 , cv2 .
THRE SH_BIN ARY_IN V +
cv2 . THRESH_OTSU )
# Find contours
contours , hierarchy = cv2 . findContours ( thresh , cv2 .
RETR_EXTERNAL ,
cv2 . C H AI N _ AP P R OX _ S IM P L E )
# Create a copy of the original image to draw contours
on
contour_image = image . copy ()
# Draw contours on the image
cv2 . drawContours ( contour_image , contours , -1 , (0 , 255 ,
0) , 2)
# Display the original and contour images
cv2 . imshow ( ’ Original ␣ Image ’ , image )
cv2 . imshow ( ’ Contours ’ , contour_image )
# Wait for a key press to close the windows
cv2 . waitKey (0)
cv2 . d estroy AllWin dows ()
Listing 11: Contour an Image
22
�12 Program 12
Write a program to detect a face/s in an image.
12.1 Code
import cv2
# Load the cascade classifier for face detection
face_cascade = cv2 . Ca scadeC lassif ier ( cv2 . data .
haarcascades + ’ h a a r c a s c a d e _ f r o n t a l f a c e _ d e f a u l t . xml
’)
# Load the image
image = cv2 . imread ( ’C :/ Desktop ␣ Folders / child . jpg ’)
# Convert the image to grayscale
gray = cv2 . cvtColor ( image , cv2 . COLOR_BGR2GRAY )
# Detect faces in the grayscale image
faces = face_cascade . detectMultiScale ( gray ,
scaleFactor =1.1 , minNeighbors =5 ,
minSize =(30 , 30) )
# Draw rectangles around the detected faces
for (x , y , w , h ) in faces :
cv2 . rectangle ( image , (x , y ) , ( x + w , y + h ) , (0 , 255 ,
0) , 2)
# Display the image with detected faces
cv2 . imshow ( ’ Face ␣ Detection ’ , image )
# Wait for a key press to close the window
cv2 . waitKey (0)
cv2 . d estroy AllWin dows ()
Listing 12: Detect a Face/s in an Image
23