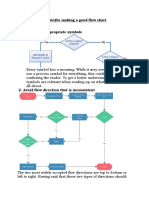
Flowchart and Flowchart Techniques
What is a Flowchart?
A flowchart is a graphical representation of a process or algorithm. It uses various symbols
to illustrate the sequence of steps, decisions, and actions required to complete a specific
task or solve a problem. Flowcharts help in understanding and analyzing a process,
ensuring clarity, and improving decision-making.
Importance of Flowcharts
1. Simplifies Complex Processes: Breaks down intricate systems into manageable steps.
2. Enhances Communication: Aids in explaining processes to team members or
stakeholders.
3. Identifies Issues: Facilitates troubleshooting by pinpointing bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
4. Improves Process Design: Helps in optimizing workflows and ensuring all scenarios are
considered.
Basic Symbols in Flowcharts
Here are some common symbols used in flowcharts and their meanings:
1. Oval (Terminator): Indicates the start or end of a process.
2. Rectangle (Process): Represents a task, operation, or action to be performed.
3. Diamond (Decision): Indicates a decision point requiring a Yes/No or True/False answer.
4. Arrow (Connector): Shows the flow of process steps.
5. Circle (Connector/Off-page link): Used to connect different parts of the flowchart,
especially when spanning multiple pages.
Flowchart Techniques
1. Top-Down Approach:
- Start with the major process or problem.
- Break it down into smaller, manageable components.
- Example: Software development process.
2. Stepwise Refinement:
- Start with a general idea of the process.
- Refine each step into more specific tasks or actions.
- Example: Writing an algorithm for a program.
3. Use of Sub-Processes:
- Create modular sections for complex processes.
- Represent sub-processes as a single rectangle, with details shown in another flowchart.
- Example: Online shopping system.
�4. Decision Trees:
- Incorporate multiple decision points using diamonds.
- Helpful for decision-based processes or algorithms.
- Example: Loan eligibility process.
5. Swimlane Flowcharts:
- Divide the flowchart into lanes representing different departments, roles, or systems.
- Each lane contains tasks performed by the respective entity.
- Example: Cross-functional team processes.
Best Practices for Creating Flowcharts
1. Keep It Simple:
- Avoid overcomplicating with unnecessary symbols or steps.
- Use clear, concise text.
2. Maintain Consistency:
- Use standard symbols and consistent shapes throughout.
3. Organize Flow:
- Flow should move from top to bottom or left to right for easy readability.
4. Label Clearly:
- Use descriptive labels for processes and decisions.
5. Validate:
- Verify the flowchart by walking through the steps to ensure accuracy.
Applications of Flowcharts
1. Programming and Algorithm Design: Visualize algorithms before coding.
2. Business Processes: Document workflows, identify inefficiencies, and improve processes.
3. Education and Training: Teach concepts through visual steps.
4. Project Management: Plan tasks, dependencies, and workflows.