TUTORIAL 1 DIODE EQUATION
The general characteristics of a semiconductor diode can be defined by the following equation,
referred to as Shockley’s equation, for the forward- and reverse-bias regions:
Is is the reverse saturation current
VD is the applied forward-bias voltage across the diode
n is an ideality factor, which is a function of the operating conditions and physical construction;
it has a range between 1 and 2 depending on a wide variety of factors.
The voltage VT is called the thermal voltage and is determined by
k is Boltzmann’s constant = 1.38*10-23 J/K
TK is the absolute temperature in kelvins = 273 + the temperature in °C
q is the magnitude of electronic charge = 1.6 * 10-19 C
Questions
1. a. Determine the thermal voltage for a diode at a temperature of 20°C.
b. For the same diode of part (a), find the diode current if Is = 40 nA, n = 2 (low value of VD),
and the applied bias voltage is 0.5 V.
2. Repeat the previous Problem for T = 100°C. Assume that Is has increased to 5 mA.
3. Determine the diode current at 20°C for a silicon diode with n = 2, Is = 0.1 mA at a reverse-
bias potential of -10 V.
4. Given a diode current of 8 mA and n = 1, find Is if the applied voltage is 0.5 V and the
temperature is room temperature (25°C).
5. Given a diode current of 6 mA, VT= 26 mV, n= 1, and Is= 1 nA, find the applied voltage VD.
6. In the reverse-bias region the saturation current of a silicon diode is about 0.1 mA (T 5 20°C).
1
�TUTORIAL 1 DIODE EQUATION
Determine its approximate value if the temperature is increased 40°C.
7. Compare the characteristics of a silicon and a germanium diode and determine which you
would prefer to use for most practical applications.
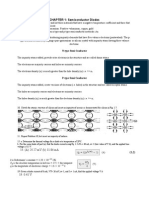
8. Determine the static or dc resistance of the commercially available diode of Fig at a forward
current of 4 mA.
2
�TUTORIAL 1 DIODE EQUATION
9. Repeat previous Problem at a forward current of 15 mA and compare results.
10. Determine the static or dc resistance of the commercially available diode of Fig. 15 at a
reverse voltage of -10 V. How does it compare to the value determined at a reverse voltage of
-30 V?
11. Calculate the dc and ac resistances for the diode of Fig. at a forward current of 10 mA and
compare their magnitudes.
12. Using the curves of Fig :
a. Determine the voltage across each diode at a current of 1 mA.
b. Repeat for a current of 4 mA.
c. Repeat for a current of 30 mA.