0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views54 pagesManual On Workshop Practice
manual on workshop practice
Uploaded by
prettysoul160Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views54 pagesManual On Workshop Practice
manual on workshop practice
Uploaded by
prettysoul160Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
You are on page 1/ 54
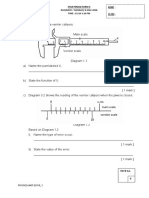
NAME OF THE JOB
. | SAFETY PRACTICE
02. | FITTING SHOP
24 |Job-01
STUD AND A SQUARE NUT
2.2 | Job-—02
DIVIDER
23 | Job-03
PAPER WEIGHT
03. |SHEET METAL
3.1 | Job-04
TAPER TRAY
3.2 | Job-05
FUNNEL
04. | WELDING SHOP
44 | Job-08
SQUARE BUTT JOINT
42 | Job-07
LAP FILLET JOINT IN FLAT POSITION
05. |TURNING SHOP
5.1 | Job - 08
JOB OPERATION BY S.S AND
S.C. LATHE
CNC MILLING & LATHE MACHINE
Assignment Mark :————-—
Sessional Mark
Final Viva Marks
TOTAL MARKS
01-03
04-19
20-22
23-25
26-28
29-30
31-33
34-36
37-39
40-42
43-45
46-49
50-52
53-55
DATEOF | GRADE/| SIGN. OF | REMqz,,
EXPERIMENT | MARK | SUBJECT
PERFORMED LECTURER
= a
Signature of the H.0.D./Lect
Of the Department
somehow be involved in an “accident” or “injury’
here danger i Y
art shop depends on the hazard and risk involved with machi
that an injury will occur. eae
The causes of injury are varied, but they involve the following facto}
va.
b.
“Fem pan
4
National Standards Institute, Safety
im the workplaces such as :
INTRODUCTION :
a
wane
respect for the equipment being used
ni
Fe res0o9
he.
ine or industrial or consumer prod
i Safety” is a judgement of the
inati and risk. Thus, the safety o
is the combination of hazard Pe toh Horeca
ifs generally recognized that there is no ma
ws such a
Having part of the body caught in or between machine components.
Being struck by an object.
Falling from equipment, structures, or ladders.
Slipping or tipping on floor surfaces.
Explosions and fire.
Exposure to high voltage electrical wiring and switch box.
Burns with or exposure to temperture extremes.
Exposure to or injection of toxic, chemicals,
Excessive physical strain. “ Sl
Protection of eyes from metal chips. %
In United States, various safety and health standards have been promulgated b'
iterature is available from the National Safety Ca
ie Created the folloiwng hierarchy for treat
Safety professionals and organizatio
Reduce the danger to a reasonable level through design.
Apply safeguarding technology.
Use warning signs and label,
Train and instruct the workers.
Prescribe personal protective Safety equipment
(grooves, goggles, apron, shoes etc.) _
All workshops and work-areas are : i
Places of some risks, but a health: :
n : regard for the
reduces the risk of an accident considerably.
Sollowing are the golden rules of safe work-practices such as «
If you open it, close it,
If you turn it ‘ON’, turn it ‘OFF’.
If you unlock it, lock it,
If you break it, repair it
If you can’t fix it, call in some one who can,
If you make a mess, clean it up.
If you move it, put it back.
If it doesn’t concern you, leave it alone.
i Provision of proper fencing around dan,
: \gerous/ hazardous activity centre
Devices : i
i. Pull-back mechanism for the operator's hands
wi, Deadman Controls — A system in which the power is automatically shut off in the event of
‘operator becoming senseless or collapsed.
__ iti, Presence of sensing devices.
‘Safety During Maintenance of Machinery :
> Normally, safety devices are temporarily removed during maintenance. It's the Employer!
_ Manager's responsibility to ensure. The maintenance personnel are competent to interact with the
types of hazards expected and supposed to perform the maintenance in a safe manner. The
Maintenance staff should be familiar with safety practices related to their activities.
Warnings :
Sign Post, signals and instruction charts warn the worker about sudden hazards, danger control
methods, or non-obvious consequences. The format, size, colour of warnings have been prescribed
by Industry Standards and ISI codes.
Personal Prtoective Equipment :
Goggles, face-shields, earplugs, helmets, resit
_ protective equipment that reduce worker's exposul
‘SAFETY IN WORKSHOP : <
“ The first duty of the Manager or Instructor in a 40 brief a student or worker about
various safety features and make them aware of various safety precautions to be observed while
working on a particular machine/ machine tool. They should be sufficienctly briefed about causes/
sources of injury or accidents and how to guard against them
_ Some of the Common Sources of Accident in Workshop are as Following :
a. Revolving parts like shafts, spindles, tools etc.
b. Projecting sharp edges of belt/ chain/ pulley joints/ fasteners etc.
¢. Revolving paris like gears, rollers, friction wheels, drum, crushers etc.
- d. Contineously rotating parts like fans, open-arm pulleys, gear trains etc.
e. Converyors and mixers.
f. Grinding wheels and stones.
_ g. Reciprocating parts/ tools.
h. Intermittent feed mechanism.
i. Moving cranes/ trolleys/ welding machines.
|. Bare cables, joints, swtiches, switchboard etc.
(COMMON METHODS OF PROTECTION IN A WORKSHOP :
Some Common Methods of Protection in a Workshop are Discussed Given Below :
By Design :
When a new machine is designed, suitable housing should be designed as safety guards.
For Example : i. Belt Drive/motor in a lathe or milling machine are enclosed in a housing.
ji, _Allcontrol panels/handles should be carefully located to ensure adequate safety.
HO2N
FITTING SHOP |
ents may be prodcued by working on metal either on a machine tool or on the bench.
it becomes necessary to replace or repair a component which must fit accurately with
‘component on re-assembly. This involves a certain amount of hand fitting.\The assembly of
ine tools, jigs, gauges, ete. inviolves a certain amount of bench work. The accuracy of work done
upon the experience and skill of the fitter{Metal removal at the bench requires the use of a
‘of simple hand tools and considerable mantal effort. Working on components with hand tools
u Mostly on work benches is generally refered to as, ‘Fitting Work’ JThe hand operations
‘work consist of filing, chipping, scraping, sawing, drilling, tapping, grinding etc.
S AND EQUIPMENT REQUIRED IN THE FITTING SHOP :
the bench work and fitting require the use of a number of simple hand tools.»
and Measuring Tools :
en dimensions are given in drawing without any indication about the tolerance, it has to be
that measurement are to be made with a Steel Rule, which is used for measurement of
Itis usually graduated in millimeter and inches: It's least count is 0.5 mm or 1/64 of an inch
|Rulles are made of spring steel or stainless steel. The surface of the steel rule is stain — chrome
d to reduced glare and to prevent rusting, a
with a Steel Rule : LENGTH TO BE
"The given figure indicates the method of using a try ne
‘square and a steel rule for accurate measurements. It is
to read vertically and avoied errors arising out
_ of parallax for accurate readings. The steel rule
are accurately engraved, with line thickness
ranging from 0.12 to 0.18 mm.
‘PRECAUTIONS {
2. For maintaining the accuracy of a steel rule, it is important that to see it that its edges and
surfaces are protected from damage and rust.
b. Do not place a steel rule with any cutting tools.
c Apply a thin layer of oil when not in use.
el tool used to scribe or mark lines. It is made of steel or high carbon
| wire of 3 mm to 5 mm, whose one end is straight and the other is bent at about 90° Angle. Its
h varies from 150 mm to 300 mm. Both its ends are pointed. There are Five types of Scribers
0 ee. Improved, Adjustable Sleeve, Pocket and Knok Scriber.
a Pacarater are ue be handled very carefully!
rk on the point when not in use to prevent accidents.
me i ut perm:
Punch is a marking too! used in order to make certain dimensional features of the layot
Basically, there are two types of
punches such as : Dot and Centre
Punch.
Centre Punch :
Centre Punch as made of high
carbon steel. The angle of the point
is 90° in a centre punch and the . a
punch mark made by this is wide and not very deep, which is particularly used for locating 4 eS. Is
length is from 35 mm to 125 mm. and its wide is from 4 to 12 mm. If this centre is not made bj ‘the
centre punch, then there are chances of slipping of the point and drilling at a wrong point, whi
shown as the given figure.
Bot Punch :
Dot punch is used in order to lightly
indent along the layout lines to locate
centre of holes and to provide a small DOT PUNCH
centre mark for divider point etc. The ee ae ae
main difference is that its point is at 60°Angle. Its length is from 80 mm to 100 mm. and its thick’
from 3 mm to 5 mm/ which is shown as given figure. There are also different types of punches
available such 2s : Solid, Hallow, Pin, Bell, Prick and Automatic Punch.
ARECAUTIONS : =)
(CENTRE PUNCH
@ Donotuse an ordinary punch ona hard metal,
b. Use a punch after seeing its angle. 3
& Ifthe point of the punch is damaged, then itshould be repaired and the
G. Selection of punch should be made according to the make-up of the job or metal
punch should be
ARY SQUARE :
‘Try Square is used for measuring right angle ofa job and for checking |
216 used in engineering field can be divided into Three parts such as »
Solid, Adjustable and Diemakers try square. The accuracy of
measurement by try square is about 0.002 mm per 10 mm length which
is accurate enough for most workshop purposes. anne
PRECAUTIONS :
. fe shoul
a, eee ne ute try square as a hammer ive. we should not use it to hit any job otherwis.
b. Try square should be kept away from cutting tools,
c. It should be cleaned properly before use,
d. After making its use, it should be kept after applying grease.
IRFACE PLATE :
Surface Plate is used for marking purpose. The
the surface plate and marked with the help of
made of cast iron. It is usually rectangular in s}
Job is placed over!
bhevel protractor. 1 is
shape.
IS:
marking or measuring a job, its Surface should be properly cleaned with a soft paper.
le using it, it should not be hit as there are chances of damage to its surface.
‘order to make the marking of the job permanent it should not be used as a table.
Cutting tool should never be used on it.
. i
___ Angle Plate is placed over the surface plate for supporting
ps at the time of marking. It is made of cast iron. The angle
_ plate is built at 90° Angle which has rectangular grooves. Both
‘of heavy jobs, nut bolts are fitted in its grooves and marking is
done. Angle plate is of two types such as : Fixed angle and
Adjustable angle plate.
S:
a. Angle plate should be carefully handled and maintained.
b. Any nicks or scratches can spoil the accuracy of the angle plates.
© Inorder to make the marking of the job permanent it should not be used as a table.
CALIPER :
“The caliper whose leg bent toward the centre is called Outside CaliperjIt is used to measure the
outside diameter of a cylinder, bar etc. It is also used for transfer dimension one place to another
place by the help of steel rule.
‘Knob
Spring
:
;
a. Adjusting
Adjusting
CE Sat
~The Caliper whose leg forward to the centre is called inside caliper. Its used to measure inside
eter of a hole, bore, slot etc, It is also used for transfer dimension one place to anather place by
p of steel rule.
instrument, which is used to measure length, bredth and thickness of a job.
is used for testing the levels of flat surface.
testing Rs eg oa and flatness of plane surfaces.
SEAT Pic.
circles, arcs, laying out perpendicular lines, bisecting lines etc.
Seven
COMBINATION SET :
Combination Set is a very useful instrument having a
, combination of five different instruments in one. A
combination set consists of a rule, square head, centre
head and a protractor. This may be used as a rule, a
square, a depth gauge for marking degrees (45°) and for
the measruing and marking angles. ser
ER CALIPER : ‘
Vernier Caliper is a precision measuring instrument used for measurement of outside dia:
insitie diameter and depth. The least count of vernier caliper is 0.001 inch and 0.02 mm. Vernic
caliper is made by assembling several different parts as shown in the given figure.
®
Depth Scale
(/ METHOD OF TAKING READING : \
(a. Write that part of the scale which contains inch signs and which is on the left hand side of 0, on
the vernier scale. .
b. Look at the divisions of central distance. How’fany of them are on the left hand side of 0 of the
vernier ? Their value is 0.1 and 0.2 inch. respectively.
©. Write the small parts of the main scale. Their value is 0.025,
4. Write down the part of the vernier scale which corresponds with the main scale after careful
watching it.
The sum total ofall the four items writen above is reading of the vernier caliper.
TIONS :
a Itis necessary that there is no play in its beam and movable jaw and it could be easily.
b, After long use, the jaw-edges wear out. In such cases, it -—= —
should be regrinded,
c. A job fixed on a machine in operation should not be
measured with it.
d. Is should always be kept away from the cutting tools.
e. Itis difficult to see the part of scale. Therefore, itis advisable
to use a magnifying glass.
Afier using it, we should clean it with thinner and keep it |
Me in the case.,
IRNIER HEIGHT GAUGE :
Vernier Height Gauge is similar to vernier calipers and used
ean purpose by the help of ‘surface plate and angle
plate. It consists of scriber by which lines are scribed on the
job. In vernier height gauge, slide base remains joint with the
beam permanently as shown in the figure.
UT
‘PRECAUTIONS :
, Itshould always be used on the plain surface of the job.
While marking, excessive Pressure should not be exerted on its scriber.
f a be used on a surface plate only.
a
Atshould be used only for precision marking or measurement, __
reading should be noted down. ae
Main
IETER : 4 Seale Thimble Ratchet
| in st
| { Micrometer is a measuring instrument used for) “7” “4"""__ | Z
easuring external, internal and depth dimensions
ccurately. They are available in different ranges. Itis made |
onthe basis of nut and screw bolt. The different parts of the |
micrometer are given in the figure. There are Three types of |
micrometer such as : Outside, Inside and Depth Micrometer.
CAUTIONS : ____ MICRO METER
&. Before using it, it should be properly cleaned with a soft cloth.
6. Before use, it should be ensured that it is faultless. _
It should not be used on machines in operation or on rough surface.
Before measuring, job should be properly cleaned. x
For setting it Ratchet Stop should be used.
After measuring, it should be locked and then reading should be taken
While keeping it, anvil and spindle should be
It should be saved from water.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN CALIPER AND MICROMETER
VERNIER CALIPER MICROMETER
zemeae
. Its range varies from 0 to 48 inch or 0 to | a. Its range is limited from 0 to 1 inch or 0 to
1200 mm. 25 mm. For measurement beyond this we
require other micrometers.
. With this we can measure both the external
and internal jobs.
. We can take measurement in inches and . Different micrometers are required for
mm simultaneously. measurement in inch and mm.
|. It is easy to make and also costs less. Itis difficult to make and it costs more.
.. Measurement taken by Vernier caliper is not Its measurement is considered exact
considered very exact because its touch is because appropriateness of touch is
not always equal. Controlled by ratchet stop.
Experiences required totake measurement | +." jtis easy to measure with the micrometer.
with this caliper.
|g. Its least count is 0.02 mm. } Its least count is 0.01 mm.
‘CUTTING AND FINISHING TOOLS :
CHISEL:
Chisel is a single point cutting tool. tis used for removing surplus metal or for cutting sheets. The
tools are made from 0.9% to 1.0% carbon steel of octagonal or hexagonal section. Chisel is used to cut
flat round or angle iron and 1/8 inch fitness of metal sheet, it also used to removed for unwanted metal
from the surface of a job by cutting it in bits and smalll pieces, this act is known as chipping, cutting
1 WBN
Different micrometers are needed for
taking measurements.
done by chisel is rough, therefore chisel are used to both
hot and cold metal. The different types of chisels are
available as shown in the figure as follows :
A InLineAsphalt Cutter B. NailPoint
C. Cross-CutAsphaltChisel D. In-Line Chisel
E BuntToo! F Tamping Pad
G Cross CutChisel H. Moil (Conical) Point
1 Cross-CutWide Chisel J. Inne AsphaltChisel
METHOD OF USING CHISEL :
a rn marking should be done on the metal to
cut.
b. Always hold the chisel properly with your left hand and the hammer in your right hand.
©. Set the chisel properly on the marked line then strike the hammer on its head. Before striking
the second blow on the chisel, it should be set again.
&. While cutting with a chisel we should conentrate on its cutting edge.
©. Strike the hammer blow at the centre of the head of chisel.
METHOD OF CHIPPING :
@. Select the chisel with appropriate cutting angle according to the metal.
b. _Ifjobis:smallin size and it has to be heldina vie we should use a wooden block under the job
©. While chipping we should stand to thé left of vice\and near the bench.
¢. We should hold handle of the hammer from its end, aise it up to the height of our neck and then
strike a blow. =|
©. Chisel should be inclined towards the user at an angle of 40°, while chipping.
f. Ata time we should not chip any metal more thar’2 or 3 mm. Otherwise the edge of chisel may
be demaged.
g. If the surface to be chipped is broad, before using a cross cut chisel, we should make a groove
on the job by making a cut.
h. Only a flat chisel should be used for chipping.
While chipping after hitting the chisel with a hammer three four times, we should withdraw for a
while and then chipping.
While chipping a job held in vice we should strike the hammer blow in the direction of its
stationary jaw.
PRECAUTIONS :
a. At the time of chipping we must always use safety goggles.
b. Keep your face towards the wall, while chipping.
c. If someone is working in your front, you should fix chipping guard at the rear of vice so that
i
chips do not hit him. ;
d. While chipping we should keep on applying grease on the edge of the chisel,
HACKSAW =
Hacksaw is a multi-point cutting tool. It is used for cutting }~/
metal by hand with a frame which holds a thin blade, finally in
ition, The blade has a number of cutting teeth. The number
of teeth per inch is selected on the bit of types of job. Hacksaw
is a hand cutting tool, inorder to cut metal rods, pipes, plates or
sheet of varied thickness. It can be operated by hand or by power.
“on
‘Mainly, itconsists of two parts such as : Frame and Blade. [tis available at 300 mm of length of blade.
jis two types of Hacksaw such as : Fixed and Adjustable Hacksaw,
OF USING HACKSAW :
‘Selection of hacksaw blade should be done according to the metal for which itis to be used
i ere tec onthe frame it should be ensured that its teeth should cut the metal when they
Job should be held in the vice in such a way that its cutting lines are clearly visible
| Before starting a cut with hacksaw blade, blade should be kept on the marking line, the left hand
© thumb should be placed withits support. ° eae
You should stand on the left hand of the vice and keep your right foot backward and the left foot 2
little ahead of the right. bg
-& The speed of operating hacksaw should be 40 to 50 strokes per minute.
4% Pressure should be exerted on forward stroke and it should be withdrawn on backward stroke.
PRECAUTIONS :
Hackasw blade should be fitted on the frame very carefully.
Ttshould be neither be very tight nor very loose.
The job which is to be cut should not be held in a vice much high otherwise there would be
vibrations in it.
Hacksaw blade should not be allowed to become slanting while using a hacksaw. If it becomes
slanting, there are chances that it may break.
Ifa blade get broken while working, then we should replace it with a new blade.
If necessary, water should be used as a coolant.
After using a hacksaw either its blade should be taken out or it must be made lose.
SCRAPER : : -
‘Scraper is a cutting hand tool,
which is used to remove the high
spots left after machining has been
done on a job. Scrapers may be fiat,
triangular and half-round. The |
material is a good quality forged steel
and cutting edge is usually left very — $$$ $$$ —
hard. Scrapers are made in a variety of lengths from 100 mm onwards and in many shapes. Scrapers
‘are used whose length is 100 mm to 250 mm and there thickness varies from 1 mm to 3.5 mm.
METHOD OF USING HACKSAW :
’@. We should have our right hand on its handle and left hand on its body.
'b. While using a scraper it should be bent at about 30° angle.
‘¢. We should not keep a stroke of the scraper tool long.
d. After scraping once, scraper should be driven at right angle.
‘Scraping should be considered accurate only when the colour of paste start appearing on the
entire surface.
PRECAUTIONS :
a. ee ear fe erentement i he foh
should have proper edge.
Gant should be free from any ees tote. while scraping,
Scraper should not be used without ‘
Scraper should be kept separate from other tools.
After scraping surface should be properly cleaned,
WA0N
ere a sep
TAPS AND TAP WRENCHES :
ae a
bam « | ere
r ‘SECOND TAP :
SECOND TAP |
|
THIRD TAP
FIRST SECOND THIRD |
TAP TAP TAP THIRD TAP
LLL)
Atap isa thread cutting tool, which is used for cutting internal threads in @drilled hole. Hand tap:
are usually supplied in sets of three for each diameter and thread size. Each set consists of a taper tap
intermediate tap and plug or bottoming tap. Taps are made of high carbon steel (HCS), high speed
steel (HSS) and Aloy steel. The upper portion is square and four flutes are made on the entire partir
which threads are formed. Taps is of three types such as : First, Second and Third taps.
TAP WRENCH :
Tap wrench is a tap holding device, which is used to hold
the tap strongly and tightly. There are Three types of tap
wrenche such as : T-type, Fixed and Adjustal
METHOD OF CUTTING THREADS WITH TAP :/
. Bore a tap drill hole of appropriate size for the tap.
\
a. ta \ Z|
b. Chamfer or file the drill at the tap. a)
¢. Hold the job firmly in vice etc. ‘ j
d. First of all, use the taper tap for cutting threads. i B
@. After moving two or three threads ensure through the try square that tap is movig straight
f. Tapping should be done by moving the tap forward and backward.
g. Adequate lubricant should be used while tapping.
h. After moving the taper tap, intermediate and finishing tap should be moved.
i. While cutting threads in blind hole in between tap should be taken out to clean the metal particles.
PRECAUTIONS :
Tap drill hole of appropriate size is essential before tapping.
Use tap handle according to the tap.
Tap should be moved forward and backwards and we should prevent any jobs.
i, Tap should be cleaned properly and kept safely.
DIES AND DIE-HOLDERS :
Dies are the cutting tools used for making external threads. Dies are made either solid or split
type. They are fixed in a die-holder for holding and adjusting the die-gap. They are made of tool steel
orhigh carbon steel. There are three types of dies such as : Circular Split, Half and Adjustable Screw
plate Die.
METHOD OF USING DIE : E
2. Before cutting outer threads, the end of pipe or fod should be chamfered with a grinder ora file.
b. For cutting threads on a pipe, rod or any other job it should be firmly held in a vice.
wa
aogD
e wile fitting die in ajob only the side of tapered threads should be fitted.
ie After fitting the die on the job you should adjust it according to your requirement.
¢, Keep on moving the die forward and backwards.
4, Equal pressure should be exerted on the die handle.
Jobs of large diameter, threads should be cut after adjusting two-three cuts.
Proper lubrication should be used while cutting threads.
i After cutting the threads, it should be checked with a nut or ring gauge.
j_ After using the drill. It should be properly cleaned and replaced at its proper place.
Centre Screw
a Side Screw Side Screw
/ Die Stock
Button Stock A
Pattern Z
CIRCULAR SPLIT DIE HOLDE
HALF DIE
COMBINATION PLIER :
Combination Plier is a mechanical
multipurpose tool, which is used to bend,
cut and scrap the insulation of cables
having lenath of 15 or 20cm, anda P.V.C. }
‘of rubber sleeve is covered on its arms
‘as shown in the figure.
TWIST DRILL AND DRILLING MACHINE :
" Diillingis a process of making holes on a workpiece. The tool used for boring hole is called dri bit,
‘he machine with which the dril is moved is called drilling machine. The process of boring holes with dri
“and diling machine is called driling. Various types of driling machines are available such as : Sensitive,
_ Pillar type and radial type drilling machine. The folloiwng are the sizes and designations of twist drills.
& Wg wren
From 1/16" onward
a er ae
|_Numberarits 7 E
Taper shank drills
METHOD OF DRILLING :
@. Drill should be choosen according to the material and the hole to be bored in it. It should hay
appropriate edge and all its angles should be well edge and all its angles should be well grinde
Drill should be properly fitted in the spindle or chuck of the drilling machine.
‘Speed of the machine should be set according to the metal of the job and diameter of 1!
Job should be properly gripped in the machine vice or other medium.
At the place where hole is to be made, marking should be done with the centre punch.
Place the drill straight in the place of centre punch and check.
If a blind hole is to be bored, set the depth of the drill with the machine.
Place the drill exactly in the centre of drill punch mark.
If the drill is operating exactly in the centre, speed can be given.
Use of lubricant and coolant is essential to get clean and proper finish and to save the drill from
vrpeseaos
Cutting angle and clearance angle ete. of the drill should be grined according to the material .
Speed on the machine should be set according to the metal and the diameter of the drill.
Ifa hole of large diameter is to be bored, first the kote should be bored with a small drill.
While drilling, a wooden socket should be placed below the job so that drill may not damage th
‘machine bed by going across.
Drifi should be used to separate drill from the machine.
Filing is one of the methods of removing Wa
small amount of material from the surface of }S
a metal part. A file is a hardened steel tool,
having slant parallel role of cutting edges or
teeth on its surfaces. On the faces, the teeth |
are usually diagonal to the edge. On end of } %
the file is shaped to fit into a wooden handle. |
The hand file is of parallel width and tapering
slightly in thickness, towards the teeth. It is
provided with double cut teeth on the faces, single cut on one edge and no teeth. It is Provided with
double cut teeth on the faces, single cut on one edge and no teeth on the other edge, which is known
as the safe edge. Files are Classified according to the basic of length, shape, grade and cut.
LENGTH OF FILE :
According to the length, a file is measured from heel to tip. It is available from 100 mm to 450 mm.
_BHAPE OF FILE :
Different shapes of file are used for different shape of jobs and it is
classified as follows,
Round, Halt-round, Triangular, Hand, Neodle and Knife edge file as sh eee Fiat,
own in the given figure.
MAB
HOLE FILE
ROUND FILE
HAND FILE
ALE ROUND FILE
FLAT Fike KNIFE FILE
determined on the basis of distance between
#8 of diatance between the tooth of tho file (TPH), On the
basis Gf thoso teath tholr grades are made, On tho basis of the number of teeth on a filo, it is
Glassified such as: Rough, Bastard, Second-cut, Smooth and Dead Smooth tile.
ROUGH FILE ASTARD FILL _SUCOND CUT LL SMOOTH FILE___DIAD SMOOTH FILE
_2UT OF FILE:
foront shapos and types. Acéording to the cut, they are cl
The tooth cut on the files are of diff
Ingle-cut, Doublo-cut, Curved-cut, Splral-cut and Rasp cut Filo
DOUBLE CUT SINGLE CUT RASP CUT
“yfferHoD OF FILE:
fed
Choose the right type of file, according to the job.
of th fila, In small {iles, a small handle should be
There should be handle fitted on the tang
ze fitted and a larger handle in larger file, Otherwise the
power ‘would be unnecessary wasted.
c. Hold the handle of the file with the right hand and keep the file end balanced with the left hand.
d, Atthe time of filing, left leg ‘should be kept ahead and tho right leg a little behind.
@. Pressure on the file should b ‘exerted while moving it ahead, not while driving hack,
f, Only your hands should move with the file and not your whole body. As far as possible, keep
jour body still
ae ‘ ‘ile should be at the rate of 30 to 35 strokes por minute. 2
i ‘Speed of movng the fi
IONS +
Select ing to the job.
Beas coring According to thesize, complete handle should be fixed on the file.
ut
While filing a sheet, we should cut it in length,
Wial
halance of the file would not be proper and
oe
d. Keep the file away from other tools. They should not be heaped together.
e, File should not be heated.
L Donot apply oil or grease on the file. )
HOLDING . DEVICE
FICE :
fi A ‘Vice is a totaly holding device, which is use to hold the job strongly and tightly'to perform the oe
types of operations such as : Filing, Drilling, Chipping, Milling and etc. For different types oF work,
different types of vice are used such as : Bench, Machine, Pipe, Leg and Hand vice.
BENCH VICE : vapLe HARD JAWS
The vice, which is used for bench workisknown as | ~ saw ti ote UAW
the bench vice. Bench Vice is made of cast iron or cast
steel, which is used to hold work for filing, sawing, | spivpLe
threading and other hand operation. It consists of two
jaws, ie., one fixed jaw and another movable jaw. When
the vice handle is turned in clockwise direction, the
movable jaw forces the work against the fixed jaw. The
job is held in between the two jaws at the time of filing,
sawing and chipping. The size of the vice is-speci
by width of the hard jaws.
PIPE VICE
/ PIPE VICE :
Pipe Vice is ued for holding cylindrical jobs (pipes and tubes). In this case,
_moves in vertical «xis. It is used for holding pipes at the time of cutting and facie a
/ MACHINE VICE .
Machine ice is used to hold a job strongly for carring out drilling, millin Y
For fastening iton the table ’ bolts are used, which fasten the viee firmly ean een.
made in the ble. Machine vice are classified based on holding the job such as : Plane. Flanged.
swivel, Unive ‘sal and Vertical machine vice. : , Flanged,
/LFG VICE: . .
Leg vie: is a holding device, which is used in black-smithy shop. Hot job -
bl ck-smit’ / operations like forging, bending and etc. done by the leg vice, eet pae rt
banch ina —nging manner. It contains one leg which is straight way placed on wood.
beled’ * are joined with each other through a hinge is entred body Is made of enone
WASH
ice is very similar to leg vice with a long leg and opens like leg vice. The hand vice is used
fivets, Keys and small drills and other similar objects which are too small to be
Mice; Only small jobs can be held in the vice. It can not be fitlad on a work bench
€ a wing nut is used which is attached on the spindle fixed between the two jaws.
‘be fastened nearly at the centre and it should not be very high from the surface of the vice.
g ‘care should be taken to ensure that the blow of hammer should not hit the vice.
h be tightened in the jaw only by moving the handle manually. A hammer should not be used
purpose.
‘Should be held in the jaw with a wood packing otherwise at the time of filing etc. chattering
rusing the vice it should be cleaned. While cleaning it should be ensured that the tiny particles of
‘do not go into the spindle.
is arectangular block, which has a ‘V' shaped groove on its upper
Hwhich is shown in the given figure. The angle of the:'Vis during layout
surements or for measuring operations. Heavy round jdbs‘are kept over
|. There is no provision to clamp the job since becalige of heavy |
{of the job, it remains fixed. { t
fobs or two-three machine parts
Tool-makers and 'C’ Clamp.
TOOL MAKER,
~ CLAMP
ch ‘screw and bolts are fitted. In both the jaws these are |
direction. These jaws are brought closer or their distance
shape of the ‘C' Clamp is ike the english letter'C’ Its a |“ pS CAME
made of mild steel. On one of the frame is made flat and
end threads are cut. It is made round in shape. Job is held |
n flat side of the clamp and the swivel tp, According the
|, which is used to beat or striking blows on jobs or metals or for driving
‘or bend a job made of metal. In addition it is also used for
also used to cut hard wires with the help of a chisel as shown
of are used in
types of hammers engineering fields such as : Ball
s Hammer, Claw Hammer and Soft. Hammers are named depending on
a ‘specified by their weight. A ball peen hammer has a flat face, which is
da ball end, particularly used foraiveltg:
fits Ms
» BALL PANE HAMMER CLAW HAMMER
STRAIGHT PANE HAMMER, SOFT HAMMER
CROSS PANE HAMMER B MALLET HAMMER
SPANNERS = = ie
A spanner is a tool used for tightening and opening nuts and bolts. It is usually made of forge
steel. They are named accoridng to their applications. The size of the spanner denotes the size
the bolt on which it can work. Generally, spanner are made of drop forge steel or carbon steel
workshop, ‘there are different types of spanner are used such as : Single ended, Double ende
Ring, Socket, Box, Combination, Hook, Adjustable, “T” Socket, Magneto, Allen Key and Pi
AdjustablesSpanner.
HOOK SPANNER: i
2}
4 |
|
MAGNETO SPANNER
‘
DOUBLE ENDED SPANNER
RING SPANNER
|
ALLEN KEY SPANNER |
—=»
PIN FACE ADJUSTABLE
SPANNER
Rete Sued Which is used for tightening and opening screws. The length ofits ‘bit’
Sra Tre enath of@ common sreweriveris em. General th bit made fat he tip but
the given figure. icin» bit’ and "U — shaped bit. Screwdrivers with flat tips and star are
Bee enidamese teas designed to tum screws, The blade is made of steel and available
Bees a rs. The grinding o the tip tothe correct shape is very important. APhilips(str)
aN ally designed to ft the head of Philips screw. The end of the blade is fluted instead of
ned. A serew driver has three main part such as : Handle, Shank and Blade.
HANDLE: =
Sasically, wooden or plastic handles are fixed to the screw drivers. In order to shapeithe wooden
from being broken, an iron ring is fixed to the handle.
middle part between the blade and the handles called shank on its lower part'ip or blade
On the upper part either there is a hole through which a wire is passed or this end is made
‘when this partis fixed the handle, it does ngt allow the shank to move separately. Shanks
blade is lower part of shank: It is also known as ti This part is hardened and tempered.
?
‘SCREW DRIVER :
‘a screw driver is measured excluding handle. The length of screw driver varies from 50
"to 18”. Different types of screw drivers are available such as : Ordinary Flat, Offset,
Watch Maker and Carpenter Screw Driver.
boring holes in metal or wood, dil and driling machine
4, where dil is a too! which is fitted in a drill machine
‘When the drill rotates on the metal it bores a
‘drilled for fastening parts with rivets, bolts or
internal threads. It is the most versatile machine
shop for the purpose. 5 q c
types of drills are used for boring holes in
HAND DRILLING MACHINE RATCHET BRACE DRILLING MACHINE
ELECTRICAL HAND DRILLING MACHINE PNEUMATIC DRILLING MACHINE ©
SURFACE GRINDER :
A surface grinder having an emery wheel is generally used in a fitting shop and is useful in removing
waste metal and sharpening drills, chisels, and other cutting tools. The hardness or softness of the whee
is dependent on the amount and kind of binding material used. For this grinder, the job is held directly by
magnetic chuck or work table race-protecting table of plaining or shaping machines also used. According
to the spindle, they are of the following type such as : Vertical-and Horizontal Spindle Grinder.
HORIZONTAL
BENCH GRINDER SPINDERGRINGES SURFACE GRINDER
SAFETY AND CARE OF GRINDING WHEELS :
Before fitting a new ginding wheel, it should be verified that there are not cracks.
Grinding whee! can set broken in case of a fall. Therefore, these should be handled carefuly.
Grinding wheels should not be used without flange.
While using wheel dress alertness should be observed else they would be broken.
Grinding machine should be fitted property.
Grinder should not be moved at more than the fixed speed.
As far as possible ginder wheel should be used from side,
As far as possible, grinder wheel should be covered, when not
in use.
POWER HACKSAW 7
Power Hacksaw is quite similar to hand hacksaw with the
addition of a suitable driving mechanism. The drive is by a belt driven
electric motor. Suitable mechanisms are provided whereby the length
of the stroke and the weight applied may be varied.
Wight
ROLLNO.
REGD. NO.
MARKS COMPLETE -..
AIM OF THE EXPERIMEN
To Prepare a Divider :
OBJECTIVES OF THE EXPERIMENT :
a. Use hacksaw to cut the required material after marketing.
». File the material to obtain the required Dimension
cc. Join two components by riverting.
SET UP OF JOB:
Equipment Required :
SL. NO.| NAME OF EQUIPMENT. SPECIFICATION / TYPE (QUANTITY
04 Bench Vice Los, 425mm
02 TrySquare 100mm
03 File Flat bastard 300mm |
04 File flat second cut 250mm
05 File half-round 150mm |
06 File triangular 150mm
07 “f Hacksaw frame with blade 300mm, |
08 ‘Surface plate 500 x 500 x 25 mm
09 Scriber 150mm
10 Centre punch 100 mm
11 Ball Pen hammer 200m
12 Radius and fillet gauge
13 Dring machine with machine vie
14 HSS. Drill Bit émm
15 Spring divider 150 mm,
16 Chisel fiat 400mm
Ramaterial Required :
a. MS. Sheet 110 x 202mm As Per Specified Given Job Diagram.
b. MS. Rivet6émm : As Per Specified Given Job Diagram.
n23u
Sen
INTRODUCTION ;
Many engineering and household articles such as bones, cans, funnels, duets etc are mad:
2 flat sheet of metal, the process being known as tim smithy. For this, the development of thear:
first draw on the sheet metal, then cut and folded to form the required shape of the article. The
of the article are then secured through welding, brazing, soldering and riveting etc.
HAND TOOLS:
Sheet metal worker does most of his job with the help of hand tools. These hand tools a
a.| SheetMetal Hammer | b.| Scriber c.| Rule a] Divide
.| Trammel f. | Stee! Square g. | Chisel A
i. | Pliers i. | File k. | Snip 1
BENCH PLATE BULLET FACE HAMER MALLET HAMMER
= G
a Tua ra A
‘STEEL RULE a Ne: E EB) |
WACHINE SHEAR ala) |
STEEL SQUARE |
SCRIBER
CHISEL, ee
PUNCH i STRAIGHT SNIP |
Lightweight hammers and malllets are used in sheet metal work. Ball peer lindrical,
slightly curved face and a ball head. It is a general-purpose hammer, ibd ee ae in sheet
metal work. Cross peen hammer has a tapered peen end and is perpendicular to the handle. Mallets
used for bending and folding work. Bullet head or bullet face hammer are used to make the job made
of light sheets hollow and riveting hammer is used for revel joint Jobs in sheet metal work.
SCRIBER : This tool is used for marking in sheet metal jobs.
RULE : In sheet metal jobs a number of rules are u: i n
discussed mn G&tah inne thanteee pa ey al eter ies have bee
DIVIDER:
Divider is used in sheet metal jobs for circle marking. Withthe divider we can also do marking
the parts of a job. 5 =
TRAMMEL : This is also a marking tool which has been discussed in the chapter on “Marking Tools”
a z a = 2a
STEEL SQUARE :
For right angle marking in sheet metal jobs steel square is used. In addition, this is also used for
checking the right angle of the jobs.
CHISEL :
Several types of chisels are used for cutting metal sheets in different ways. These have been
discussed in details in chapter on Cutting Tools”
PUNCH :
Punch is used in sheet metal jobs for punching or deep marking. Their detailed description is
given in the chapter on “Marking Tools”
PLIERS :
Pliers are used for holding or cutting small jobs or wires etc. These have been described in
detail in the chapter on “Dismentalling, Assembling and other Tools”
FILE:
‘Several types of files are used for smoothing metal sheets. We can read about them in detail in
the chapter on “Cutting Tools”.
SNIPS :
Snip is used for cutting thin sheet metal up to 20 S.W.G (Standard Wire Gauge). There are
‘several types of snips available for making straight and circular cut, the most common being straight
Snip and curved or bent snip. The straight snip has straight blade for staight-line cutting while curved
‘or bent snip has curved blade for making circular cut. Both the snips are very light and can be easily
handled by only hand. These are the following two types stich as : Straight Snip and Bent Snip.
‘SHEARS
This is also used like snip for cutting a sheets but hiblsed to cut thicker sheets as compared
to snip. This is of two types such as : Stock /Shear.
SHEET METAL BENCH TOOL :
a. Vice b. Stakes c. Gro d. Bench Plate
VICE:
Vice is used in sheet metal works for holding sheets or jobs. Normally, parallel jaw vice is used
in sheet metal works.
STAKE :
; Stake is the sheet-metal worker's anvil, used for bending, seaming or forming, using the hammers
‘and mallets. They actually work as supporting tools as well as forming tools. They help in bending
_ operation. They are of different shapes and sizes to suit the requirements of the work.
The double seaming stake is used to make double seam. The beak horn stake is used for
round and square surfaces, bending straight edges and marking corners. The bevel
edges square stake is used to form corners and edges. The hatchet stake is used to make straight
* for folding and bending edges. Small tools and pipes may be formed on the needle
stake and cone-shaped articles may be formed on blow-horn stake. The hollow mandrel stake
ee tor riveting, seaming and forming.
RIVET SETS :
"Hand are used to groove and flattern a seam. This available in many shapes. Rivet
a hardened steel too! with a hollow in one end. Itis used to shape the end of a rivet into a round
0 The bench plate is a Special type of plate made of carbon steel. Different types of holes, round,
different shapes and sizes are made in this plate. Different types of stakes are fixed in
and used. ie) 53
13001
SECTION :
ROLL NO.
COMPLETE :..
Sign. of Sr
AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT :
To Prepare and Make a taper Tray :
OBJECTIVES OF THE EXPERIMENT :
a Use snips to cut the sheet for the development of a taper square tray
b Make Double Hem on the edges.
Bend the sheet on hatchet stake.
d. Soft solder lap joint.
SET UP OF THE JOB =
Equipment Required :
—$—$——— ————
NAME OF EQUIPMENT SPECIFICATION / TYPE
Steel Rule a
Folding Rule
Straight Edge
Try Square
Scriber
Divider
Punch
Chiset
Raw Material Required
a, MS. sheet : As Per Specified Given Job Diagram,
b. Soft solder : As Per Specified Given,
8A
the size of the sheet as per the sketch using a steel Rule.
the sheet on a leveling plate by a maliet.
out the development of the sheet by the parallel line method as per dimension.
‘waste material Yi
SECTION :.
ROLL NO.
COMPLETE ..........
ff ‘ Sign. of Sr. Lect/Lecturer
AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT :
To Prepare and Make a Funnel :
OBJECTIVES OF THE EXPERIMENT :
a. the sheet for the Development of funnel
b. seam on the edge
©. Bend the sheet metal on a taper bar
dF 1g a conical shape
e
if.
si
e sheet with grooved loke seam using grooves
e sheet-metal to obtain a leak proof joint.
=T UP OF THE JOB:
). OF TOOLS - ‘SPECIFICATION TTYPE - l QUANTITY
jo Stee! Rule 300mm
2 Divider |
Band Snip 1200 mm |
Chisel |
Straight edge |
Hammer
Try Square
Snip (Straight)
Scriber
ring Iron
-
Required :
: As Per Specified Given Job Diagram.
2 As Per Specified Given.
N34
imilar or dissimilar metal pieces. In this process, the two
of heat, It results in a joint that is equivalent in composition
Iding process such as : Electric Arc, Gas,
ding, the work pieces are melted along a
ced to form the joint on solidification
INTRODCUTION :
Welding is the process of joining two s!
‘metallic pieces are joined by the applicatioin
and characteristics of the metals joined. The various wel
Thermit, Resistance and Friction Welding. In gas and arc wol
common edge to their melting point and then a filer metal is introdu
In fact, welding is a quick cheap and simple technique of joining the metalic pieces.
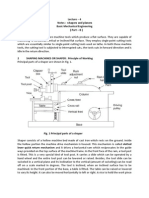
ELECTRIC ARC WELDING :
The heat required for joining the metals is obtained
from an electric arc. Transformers or motor generator
sets are used as arc welding machines. These machines
supply high electric currents at low voltage and an
electrode is used to produce the necessary arc, The
electrode serves as the filler rod and arc melts the
‘surfaces, so that the metals to be joined are actually fused
together. The given figure shows the principle. of arc
welding using a transformer. In addition to the welding
machine, certain accessories are needed for carrying out
the welding work.
WELDING CABLES :
Welding cable is used to connect the job with the earth line and
the electro holder with the main line (Phase Line). Highly insulated |
aluminium or copper cables are used for the purpose. Two welding
cables are required, one from the machine to the electrode holder and
‘the other from the machine to the ground clamp or the other negative
charge
ELECTRODES :
Filler rods used in arc welding are called electrodes. They are |
generally made of a rod of alloying elements suitable for the job, coated
with a flux. Flux acts as an insulator of electricity.
ELECTRODE HOLDER :
It consist of a handle and jaw. The electrode holder is connected
to the end of the welding cable and holds the electrode. It should be
light, strong and easy to handle and should not become hot while in
operation. The jaws of the holder are insulated,
GROUND CLAMP :
It is connected to the end of the ground cable and is clamped to
the work or welding table to complete the electric circuit. it should be
strong and durable and have a low resistance connection,
ust
Seca ea
Work Lead
for cleaning and preparing the work for
‘is used for removing slag fromed on weld:
1 is sharpened like a cold chisel and the other, toa
generally made of tool steel.
e hand type is convenient to use whenever the
hand. The helmet type, though not comfortable
OXYGEN HOSE.
WELOING ow Top Saeco
JOB NO. 06 |
SECTION b......0000
ROLL NO. :.
COMPLETE ......
‘a Lap Fillet Joint in Flat Position by Gas Welding :
at position welding,
according to the nozzle size. | «
JOB FIGURE:
PROCEDURE :
File flat and square
Clean for Welding.
Set the work pieces on welding table to form a lap joint with correct overlapping as per sk
Settthe gas welding plant and attach the nozzle.
Seta pressure of 0.15 kg/cm? for both oxygen/an acetylene gas.
Select C.C.M.S. filler rod of 1.6 mmdia. \
Wear safety apron, goggles and gloves. i
Setthe natural gas flame. J
‘Tack weld the pieces at both the ends and middle.
Clean the tacks with a wire brush and set on the welding table in flat position.
Start welding using leftward technique.
‘Stop at the left edge and fill the corner to complete the weld.
m. Extinguish the flame, coo! the nozzle and place the blowpipe in safe place.
0. Clean the welded joint and inspect visually for correct size of fillet weld,
(0. Weld the job from the other side following the above Process.
OBSERVATION
Frese sep aoe
Peer | nen]
nacdoats [Rew
|
| Quality ofthe welded | Uniform innature
| joint
| Finishing ‘Smooth witho
| __|_blowholes
COMPLETE :
Sign. of Sr. Lect/Lecturer
Sn
AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT :
To Prepare and Make a Square Butt Joint by Arc Welding :
OBJECTIVES OF THE EXPERIMENT :
a. Setthe job for square butt joint.
b. Tack weld two pieces to form square butt joint.
_Weldalong the joint with correct arc length, correct electrode angle and uniform welding spee
SET UP OF THE JO! ,
Equipment Required :
NAME OF EQUIPMENT SPECIFICATION / TYPE : QUANTITY
Are welding transformation
02 Electrodes \
Electrode holder ™~
Cable and cable connectors
05 | re hammer [
06 | Wire brush
07 —_| Welding screen or helmet
1 |
Apron 7
Pedestal grinding machine
‘Raw Material Required :
a. MS. flat : As Per Specified Given Job Diagram,
b. M.S. electrode : As Per Specified Given Job Diagram.
Wag
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS :
a
a@aogc
1
2
3.
4
5.
6.
ré
No welding apparatus should be wet or damp:
The arc should only be observed through a shied or goggles.
Use proper current capacity cables.
Remove the slagg by chipping hammer only.
After finishing the job, put the machine to off and put all other tools to beet proper places.
| ASIGNMENT QUESTIONS
Whatis Arc gap and Arc blow? iE
Name two welding defects.
Name the positions in welding
Write down the names of the different types of electric welding machine.
Write the different faults in arc welding ?
Write down the different types of arc length ?
What are the advantages of arc welding ?
—— — oa —
| WRITTING SPACE FOR ASSIGNMENT |
4s
econ :
Turning is the machining process to bring the raw material to the required, cylindrical shape and
size by metal removal from the work surface. This is done by feeding a cutting tool against a rotating
workpiece, This machine tool on which turning is carried out is called lathe.
WORKING PRINCIPLE : { ,
Lathe removes considerable materials
{rom rotating workpiece in the form of chips |
with the help of tools, which is feed against
the rotating workpiece. The tool material |
should be harder than the workpiece and the
father had surely and rigidly on the machine
| The tool may size linear machine in any
direction, Alathe is used to produce cylindrical
‘Surface and plane surface at right angle to
ite axis of rotation. It can also produce a |
taper below. /| 3
j Alathe, basically consists of a bed to/provide. support 9 head stock across side to transvers
| The tool and tool post mounted on the across the spindle |sdfiven by a’motor through the gear box
| te obtain a long speed to carriage moves over the bedside which is paralled to workpiece and
| spindle provides transverse. It was the mo: Renginedathe which is equiped well, all necessary
for acurate tool room work. It is generaily-bed driven machine with considerable range
‘spindle and feeds.
_ TYPES OF LATHE :
"Lathe machines are used in workshops can be divided into following types such as... Centre
luction, engine and Special Lathe. —<—— —- =
HE
—.. Lathe is also known as SS and SC Lathe,
the, Bench Lathe, Foot Lathe, Too! and Engine Lathe a
LATHE =
ion Lathes are used when a particular job is to be |
in a large quantity. There are three kinds of production |
chines are availabe such as : Capstan Lathe, Turret Lathe
types of lathe machines are used for specific purposes.
: Relieving Lathe, which are used are providing relief to |
s or tap. There are three types of lathe are available
ion such as : Axial turning Lathe, Copying Lathe and
WAG IT
ENGINE LATHE :
Engine Lathe machines is normally used by fitters in the
workshop, when electric motors were not invented. This
machines are operated with steam engines
MAIN PARTS OF THE LATHE ;
The following are the main parts of the lathe such as :
a. Head stock b. Tail Stock c. Carriage
d. Cross Slide €. Compounds Slide f Bed
g. Feed Shaft h. Legs Ih Lead Sc
j. Quick Change Gear Box C= Cannlage aie
HEAD STOCK: See
tis otherwise known as Live Centre. Head stock is fitted on
the lathe bed on the left hand side of the lathe operator. The required ha
gear and cone pulley is fitted in it for driving the lathe spindle. There
are two types of head stock such as : All geared and Cone pulley |
head stock.
TAIL STOCK :
The tail stock is otherwise known as Dead Centre. Itis fitted on
the lathe machines bed, én the right hand side of the lathe operator
it can be moved any désired space on the lathe bed in case of |
need. It is used for centré,to centre tuming of lengthy workpiece
CARRIAGE : Zo i
Literal meaning of “carriage” is to carry. Through carriags, a
job can be brought in contact with the Cutting tool or withdrawn from |
Such a contact. It operates on bed ways between tail stock and | mn
head stock.
CROSS SLIDE: . \
It is provided by terminal dove tail in one side and assembles se
inthe top of the saddles with its tool dove tail. Ataper grip is provided pa
with saddle and cross slide dovetail to permit required but full| |
movement of cross-section is provided with T-section to enable
fixing of gear tool parts attachment from side is generated in degree |
to failated tallated swiveling the compound next is movement on
cross-section side which is directly assembles with cross slide and | = .
be swivelted on either side to give desire angle to compound next.
COMPOUND SLIDE:
tsupports the tool post and cutting tools in its various positions. |
It may be swivelled on the cross slide to any angle in the horizontal
planes, as its has being graduated suitably. Its necessary in turning.
MAT IT
Eee
SECTION :,.
ROLL NO. :.
COMPLETE :........
Sign. of Sr. Lect/Lecturer
AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT :
To Prepare Different types of Job Operation By S.S and S.C. Lathe :
OBJECTIVES OF THE EXPERIMENT :
@ Toknowand identity the sliding surfacing and serew cutting (SS and SC) lathe machine.
6. Toknow and identify the main parts of the SS and SC lathe machine
© Toknow main functions of the different parts of the lathe machine
4.
Toknow different operations such as facing, centering, plain turning, step turning taper turning and
grooving etc.
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT REQUIRED :
NAME OF EQUIPMENT SPECIFICATION/TYPE | QUANTITY
Facing Tool
Grooving Too! |
Tappering Tool
Revolving Centre / Dead Centre
St —
t 1. a — —
MEASURING INSTRUMENT :
a. Slide Caliper b. Outside Caliper c. Steel Rule
Raw Material Required :
@. M.S. Round Rod : As Per Specified Given Job Diagram.
30 mm ——+-—20 mm—+e—— 40 mm——+le-t0 mma]
ALL THE DIMENSIONS ARE IN MM
You might also like
- Magna 18 Inch Jigsaw Model 610 Manual CompressedNo ratings yetMagna 18 Inch Jigsaw Model 610 Manual Compressed10 pages
- Metalworking Sink or Swim Tips and Tricks For Machinists Welders and Fabricators 1st Edition Tom Lipton PDF DownloadNo ratings yetMetalworking Sink or Swim Tips and Tricks For Machinists Welders and Fabricators 1st Edition Tom Lipton PDF Download58 pages
- Technical Drawing - Section and Auxiliary ViewsNo ratings yetTechnical Drawing - Section and Auxiliary Views18 pages
- Operating Instructions: Radial Drill Press R32No ratings yetOperating Instructions: Radial Drill Press R3223 pages
- Metal Working Processes, Tools, and Machines: (Sheet and Small Section Steel)100% (2)Metal Working Processes, Tools, and Machines: (Sheet and Small Section Steel)35 pages
- Milling Introduction Types of Milling MachineNo ratings yetMilling Introduction Types of Milling Machine21 pages
- Installing Gyprock Plasterboard: How To Install Gyprock Plasterboard Walls and CeilingsNo ratings yetInstalling Gyprock Plasterboard: How To Install Gyprock Plasterboard Walls and Ceilings4 pages