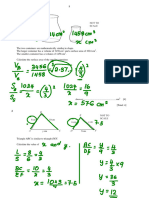
PS #1
Solution:
Using the Pythagorean Theorem,
2 2 2
x =¿ ( 12 cm ) + ( 16 cm )
x=¿ √ ( 12 cm )2+ ( 16 cm)2
x=¿ √ 144 cm2 +256 cm2
x=¿ √ 400 cm2
x=¿ 20 cm
Therefore, x=¿ 20 cm
PS #2
1 1 1
5.) Solve for y: 4 y −6 y =9 y , y ∈ R
Solution:
1 1 1
y y y
4 6 9
1
− 1
= 1
y y
9 9 9y
( ) ()
2 1 1
2 y 2 y
2
− =1
3 3
[( ) ] ( )
1 2
2 2 1y
y
− =1
3 3
� ()
1
2 y
Let x =
3
2
x −x−1=0 ; where a=1 , b=−1 , c=−1
1± √ 1 −4 (1)(−1) 1 ± √ 1+ 4 1± √ 5
2
x= = =
2 2 2
()
1
2 y
x=
3
1 2
lnx= ln
y 3
2
ln
3
y= =0.84253
1+ √ 5
ln
2
Therefore, y=0.84253
PS#3
3. If a+ b=1 and a 2+ b2=2 , find the numerical value of a 11 +b11
Solution:
a+ b=1
( a+ b )2=12
2 2 2 2
a + b +2 ab=1 , and a + b =2
2+2 ab=1
2 ab=1−2
−1
2 ab=
2
( a+ b )3=13
3 3
a + b +3 ab(a+b)=1
� 3 3 −1
a + b +3( )(1)=1
2
3 3 −3
a + b +( )=1
2
3 3 3
a + b =1+
2
3 3 3
a + b =1+
2
3 3 5
a +b =
2
(a ¿ ¿ 2+ b2 )(a ¿ ¿ 3+ b3)=(2) ( 52 ) ¿ ¿
a ( a ¿ ¿ 3+b )+b (a ¿ ¿ 3+ b )=5 ¿ ¿
2 3 2 3
5 2 3 2 3 5
a +a b + b a +b =5
5 5 2 2
a + b +a b ( ab)=5
( )
2
5 5 −1
a +b + (1)=5
2
a + b =¿ 5−
5 5
( 14 )
5 5 19
a +b =
4
(2)
2
( a 3 + b3 ) = 5
2
( a 3 ) + ( b3 ) +2 a 3 b 3= 25
2 2
6 6 3 25
a + b +2 ( ab ) =
4
( )
3
6 6 −1 25
a + b +2 =
2 4
�a 6+ b6 +2 ( −18 )= 254
6 6 25 1 26
a +b = + =
4 4 4
6 6 26 13
a +b = ∨
4 2
(a ¿ ¿ 5+b5 )(a ¿ ¿ 6+b6 )= ( 194 )( 132 ) ¿ ¿
5 6 5 6 247
a (a ¿ ¿ 6+ b )+ b (a ¿ ¿ 6+b )= ¿¿
8
11 5 6 5 6 247
a +a b + b a =
8
11 11 5 5 247
a +b + a b (b +a)=
8
11 11 5 247
a +b + ( ab ) ( a+b)=
8
( )
5
11 11 −1 247
a +b + (1)=
2 8
11 11 1 247
a +b − =
32 8
11 11 247 1
a +b = +
8 32
11 11 989
a +b =
32
11 11 989
Therefore, a +b =
32
PS#4
()()
3 3
1 1 1 a b
1. If + = and + =2 √ n , find n
a b a+b b a
Solution:
� ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )( ba )
2 2 2
1 1 1 a b a b a
+ = + = + −2
a b a+b b a b a b
( ) −2 ( 1)
2 2 2
a+b 1 a +b
= ¿
ab a+b ab
( a+b )2
=1 ¿ (−1 )2−2
ab
Also, ¿−1
( a+b )2
=1
ab
2 2
a +2 ab+b
=1
ab
2 2
a +2 ab +b =ab
2 2
a + b =−ab
2 2
a +b
=−1
ab
Note that,
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )( ba )
3 3 2
a b a b a
+ = + −2
b a b a b
( ) [( ) ( ) ( )( ba )]=2 √ n
2 2
a b a b a
+ + −
b a b a b
( )[( ) ( ) ]
2 2 2 2
a +b a b
+ −1 =2 √ n
ab b a
(−1 ) [ −1−1 ] =2 √ n
(−1 ) (−2 )=2 √ n
2 2 √n
=
2 2
1= √ n
Therefore, n=1
�PS#5
5. a.
Given:
∠ ABC=90 °
AC=√ 2
⃑
⃑
AB=1
Solution:
45 ° −45 °−90 ° TRIANGLE THEOREM: In a 45 ° −45 °−90 ° the length of the hypotenuse is the length
of a leg times √ 2.
� Thus, ⃑
BC =1
∠ BAC=45°
∠ BAC=45°
TWO TANGENTS THEOREM: If two tangent segments are drawn to one circle from the same external
point, then they are congruent
Therefore, ⃑
NC ≅ ⃑
CB, Thus , ⃑
NC =1
TANGENT TO A CIRCLE THEOREM: The angle between a tangent and a radius is 90 ° . They are
perpendicular.
By the 45 ° −45 °−90 ° TRIANGLE THEOREM,
∠ AMN=45 ° and ⃑
NM ≅ ⃑
AN ≅ r
⃑
AC=⃑
AN+ ⃑
NC
√ 2=r +1
r =√2−1 Therefore, the radius of the semi-circle is √ 2−1
b.) If α ∧β are the roots of x 2+ 3 x +1=0 . Find α 2−3 β .
Solution:
a=1 , b=3 , c=1
−b −3
α + β= = =−3
a 1
c 1
αβ = = =1
a 1
( α + β )2=α 2+ β 2 +2 αβ =(−3 )2
2 2
¿ α + β +2(1)=9
2 2
¿ α + β =9−2
2 2
¿ α + β =7
( α −β )2=α 2 + β 2−2 α ¿ α 2+ β2 −2 α β
� ¿ 7−2 (1 )
( α −β )2=5
√(α− β)2=± √5
(α −β )=± √ 5
( α + β )+ ( α −β )=2 α and ( α + β )−( α −β )=2 β
−3+ √ 5=2 α −3+ √ 5=2 β
Case 1:
−3+√ 5 −3−√ 5
α= β=
2 2
Substituting to α 2−3 β gives
( ) ( )
2
2 −3+ √ 5 −3−√ 5
α −3 β= −3
2 2
9−6 √ 5+5 9+3 √ 5
¿ + =8
4 2
Case 2:
−3−√ 5 −3+√ 5
α= β=
2 2
( ) ( )
2
2 −3−√ 5 −3+ √ 5
α −3 β= −3
2 2
9+6 √ 5+5 9−3 √ 5
¿ + =8
4 2
Therefore, α 2−3 β=8