0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views6 pagesPGDCA 106 LabPractice2 SQL2
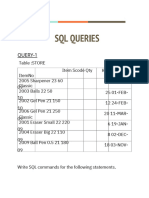
The document provides a comprehensive overview of SQL commands and their usage, including SELECT statements with WHERE clauses, LIKE, IN, and various conditional operators. It also covers commands for deleting records, creating tables with constraints, accessing records from multiple tables, and using views, joins, and subqueries. Additionally, it includes examples of ordering and grouping records, as well as using the HAVING clause.
Uploaded by
Dileep Kumar KCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views6 pagesPGDCA 106 LabPractice2 SQL2
The document provides a comprehensive overview of SQL commands and their usage, including SELECT statements with WHERE clauses, LIKE, IN, and various conditional operators. It also covers commands for deleting records, creating tables with constraints, accessing records from multiple tables, and using views, joins, and subqueries. Additionally, it includes examples of ordering and grouping records, as well as using the HAVING clause.
Uploaded by
Dileep Kumar KCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6