0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views11 pagesUnit3 - 3) Pandas - Ipynb - Colab
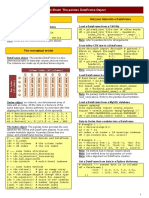
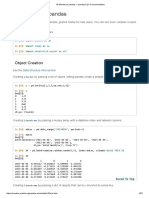
The document provides an overview of using the Pandas library in Python, focusing on data structures such as Series and DataFrame. It includes examples of creating these structures, performing basic operations, selecting data, setting values, and handling missing data. Additionally, it covers data manipulation techniques like handling duplicates and applying functions to data.
Uploaded by
shivam511439Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views11 pagesUnit3 - 3) Pandas - Ipynb - Colab
The document provides an overview of using the Pandas library in Python, focusing on data structures such as Series and DataFrame. It includes examples of creating these structures, performing basic operations, selecting data, setting values, and handling missing data. Additionally, it covers data manipulation techniques like handling duplicates and applying functions to data.
Uploaded by
shivam511439Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 11