0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views9 pagesPandas Part-2
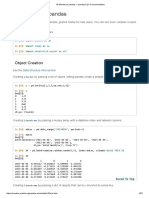
The document provides an overview of various operations that can be performed on a Pandas DataFrame, including accessing data using loc and iloc functions, filtering rows and columns, and dropping specific rows or columns. It also explains how to reset the index of a DataFrame and modify the original DataFrame. Examples of code snippets illustrate these operations using random data.
Uploaded by
imbilalbaigCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views9 pagesPandas Part-2
The document provides an overview of various operations that can be performed on a Pandas DataFrame, including accessing data using loc and iloc functions, filtering rows and columns, and dropping specific rows or columns. It also explains how to reset the index of a DataFrame and modify the original DataFrame. Examples of code snippets illustrate these operations using random data.
Uploaded by
imbilalbaigCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9