0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views17 pagesSEchap 2&3
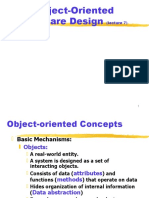
Chapter 2 provides an overview of UML (Unified Modeling Language), emphasizing its significance in software development for modeling, analyzing, and documenting systems. It covers various UML diagram types, principles of modeling, and the importance of using UML tools for effective communication and collaboration. The chapter also includes exam questions to test understanding of UML concepts and applications.
Uploaded by
danielbirhanu0374Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views17 pagesSEchap 2&3
Chapter 2 provides an overview of UML (Unified Modeling Language), emphasizing its significance in software development for modeling, analyzing, and documenting systems. It covers various UML diagram types, principles of modeling, and the importance of using UML tools for effective communication and collaboration. The chapter also includes exam questions to test understanding of UML concepts and applications.
Uploaded by
danielbirhanu0374Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 17