0% found this document useful (0 votes)
88 views34 pagesPhilippine Electrical Code (Part 1) - Introduction
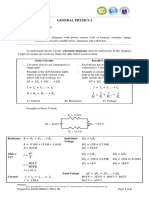
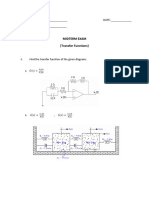
The Philippine Electrical Code (PEC) 2017 Edition establishes safety standards for electrical installations and practices in the Philippines, adopted by the Energy Regulatory Commission and the Department of Labor and Employment. Its primary purpose is to safeguard persons and property from electrical hazards, providing minimum requirements for licensed electrical practitioners. The code covers various installations, including public and private buildings, electric generating plants, and industrial facilities, while outlining mandatory and permissive rules, definitions of terms, and classifications of code rules.
Uploaded by
Junnel NegadCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
88 views34 pagesPhilippine Electrical Code (Part 1) - Introduction
The Philippine Electrical Code (PEC) 2017 Edition establishes safety standards for electrical installations and practices in the Philippines, adopted by the Energy Regulatory Commission and the Department of Labor and Employment. Its primary purpose is to safeguard persons and property from electrical hazards, providing minimum requirements for licensed electrical practitioners. The code covers various installations, including public and private buildings, electric generating plants, and industrial facilities, while outlining mandatory and permissive rules, definitions of terms, and classifications of code rules.
Uploaded by
Junnel NegadCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 34