0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesQue Es Un Esp32
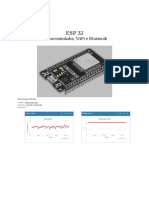
The ESP32 is a low-cost, low-power microcontroller by Espressif Systems, ideal for IoT and embedded systems, featuring a dual-core processor, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth connectivity. It supports various development frameworks and has numerous variants and development boards tailored for different applications. Common uses include smart sensors, home automation, wearables, and robotics, although challenges such as power management and complexity exist.
Uploaded by
lnvarro87Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesQue Es Un Esp32
The ESP32 is a low-cost, low-power microcontroller by Espressif Systems, ideal for IoT and embedded systems, featuring a dual-core processor, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth connectivity. It supports various development frameworks and has numerous variants and development boards tailored for different applications. Common uses include smart sensors, home automation, wearables, and robotics, although challenges such as power management and complexity exist.
Uploaded by
lnvarro87Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4