0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views5 pagesEsp32 Arduino Ide
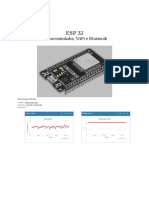
The Arduino IDE is an open-source software environment for writing, compiling, and uploading code to Arduino-compatible microcontrollers, featuring a user-friendly interface and extensive library support. The ESP32 is a powerful microcontroller with built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, suitable for IoT applications, and can be programmed using the Arduino IDE or the ESP-IDF framework. To program the ESP32 with the Arduino IDE, users must install the IDE, add the ESP32 board support, select the board, and upload their code via USB.
Uploaded by
mtsrinivas2002Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views5 pagesEsp32 Arduino Ide
The Arduino IDE is an open-source software environment for writing, compiling, and uploading code to Arduino-compatible microcontrollers, featuring a user-friendly interface and extensive library support. The ESP32 is a powerful microcontroller with built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, suitable for IoT applications, and can be programmed using the Arduino IDE or the ESP-IDF framework. To program the ESP32 with the Arduino IDE, users must install the IDE, add the ESP32 board support, select the board, and upload their code via USB.
Uploaded by
mtsrinivas2002Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5