0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesStep Up Transformer
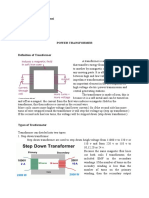
A transformer is a device used for the transmission of electric energy, specifically to increase or decrease voltage while maintaining the same frequency in AC circuits. It operates on the principles of electromagnetic induction and consists of primary and secondary coils that facilitate energy transfer. There are two main types of transformers: step-up transformers, which increase voltage, and step-down transformers, which decrease voltage.
Uploaded by
stilltushartusharCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesStep Up Transformer
A transformer is a device used for the transmission of electric energy, specifically to increase or decrease voltage while maintaining the same frequency in AC circuits. It operates on the principles of electromagnetic induction and consists of primary and secondary coils that facilitate energy transfer. There are two main types of transformers: step-up transformers, which increase voltage, and step-down transformers, which decrease voltage.
Uploaded by
stilltushartusharCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3