0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views116 pagesAdjective Types & Usage Guide
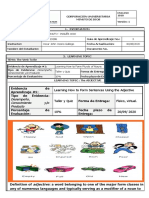
The document provides a comprehensive overview of adjectives, including their types such as proper, quality, quantity, numeral, demonstrative, distributive, interrogative, and possessive adjectives. It also explains the degrees of adjectives (positive, comparative, and superlative), rules for their usage, and common confusions among adjectives. Additionally, it covers articles, their types (definite and indefinite), and rules regarding their omission.
Uploaded by
dey.subhamoy223Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views116 pagesAdjective Types & Usage Guide
The document provides a comprehensive overview of adjectives, including their types such as proper, quality, quantity, numeral, demonstrative, distributive, interrogative, and possessive adjectives. It also explains the degrees of adjectives (positive, comparative, and superlative), rules for their usage, and common confusions among adjectives. Additionally, it covers articles, their types (definite and indefinite), and rules regarding their omission.
Uploaded by
dey.subhamoy223Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 116