05/08/2022, 17:32 What is multicast IP routing?
A Microsoft Company
What is multicast IP routing?
Topics Layer 3, Internet Protocol (IP), Reference, Network Operating System (NOS)
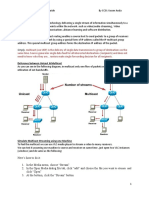
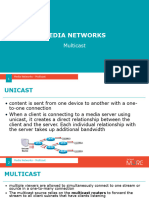
Multicast IP Routing protocols are used to distribute data (for example, audio/video streaming broadcasts) to multiple
recipients. Using multicast, a source can send a single copy of data to a single multicast address, which is then distributed
to an entire group of recipients.
A multicast group identifies a set of recipients that are interested in a particular data stream, and is represented by an IP
address from a well-defined range. Data sent to this IP address is forwarded to all members of the multicast group.
Routers between the source and recipients duplicate data packets and forward multiple copies wherever the path to
recipients diverges. Group membership information is used to calculate the best routers at which to duplicate the
packets in the data stream to optimize the use of the network.
A source host sends data to a multicast group by simply setting the destination IP address of the datagram to be the
multicast group address. Any host can become a source and send data to a multicast group. Sources do not need to
register in any way before they can begin sending data to a group, and do not need to be members of the group
themselves.
There are many different multicast protocols and modes of operation, each optimized for a particular scenario. Many of
these are still at an early stage of standardization. However, they all operate in the same general way, as follows.
A Multicast Group Membership Discovery protocol is used by receiving hosts to advertise their group membership to a
local multicast router, enabling them to join and leave multicast groups. The main Multicast Group Membership Discovery
protocols are Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) for IPv4 and Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) for IPv6.
A Multicast Routing Protocol is used to communicate between multicast routers and enables them to calculate the
multicast distribution tree of receiving hosts. Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) is the most important Multicast
Routing Protocol.
The multicast distribution tree of receiving hosts holds the route to every recipient that has joined the multicast group,
and is optimized so that
multicast traffic does not reach networks that do not have any such recipients (unless the network is a transit network on
the way to other recipients)
duplicate copies of packets are kept to a minimum.
https://www.metaswitch.com/knowledge-center/reference/what-is-multicast-ip-routing 1/2
�05/08/2022, 17:32 What is multicast IP routing?
Learn more: download the IP Routing: Multicast datasheet.
A Microsoft Company
©2022 Microsoft. All rights reserved.
Legal Notices
Terms of Use
Privacy Policy
Cookie Policy
GDPR Compliance
UK Gender Pay Gap
Modern Slavery Statement
https://www.metaswitch.com/knowledge-center/reference/what-is-multicast-ip-routing 2/2