0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views4 pagesAbdominal Study Notes
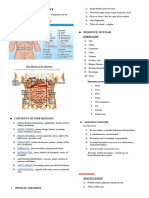
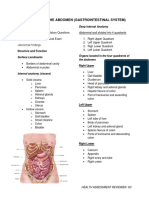
The document outlines the anatomy and physiology of the abdomen, focusing on the digestive system, including the GI tract and accessory organs, and the processes of digestion, absorption, and elimination. It also covers normal and abnormal findings during abdominal assessments, including inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation. Additionally, it details special abdominal tests for conditions such as ascites and appendicitis.
Uploaded by
Vincent Rudzlieh Mayola RamosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views4 pagesAbdominal Study Notes
The document outlines the anatomy and physiology of the abdomen, focusing on the digestive system, including the GI tract and accessory organs, and the processes of digestion, absorption, and elimination. It also covers normal and abnormal findings during abdominal assessments, including inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation. Additionally, it details special abdominal tests for conditions such as ascites and appendicitis.
Uploaded by
Vincent Rudzlieh Mayola RamosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4