0% found this document useful (0 votes)
131 views14 pagesC Programming Question Bank Answers
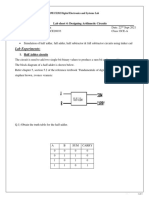
The document provides a comprehensive overview of C programming concepts, including algorithms, flowcharts, basic data types, control structures, and operators. It includes examples of code snippets for various functionalities such as checking even/odd numbers, simple calculators, and conditional statements. Additionally, it covers the structure of a C program, type conversion, and the use of flowchart symbols.
Uploaded by
mahaveeranandu03Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
131 views14 pagesC Programming Question Bank Answers
The document provides a comprehensive overview of C programming concepts, including algorithms, flowcharts, basic data types, control structures, and operators. It includes examples of code snippets for various functionalities such as checking even/odd numbers, simple calculators, and conditional statements. Additionally, it covers the structure of a C program, type conversion, and the use of flowchart symbols.
Uploaded by
mahaveeranandu03Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 14