0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views2 pagesHuman Development
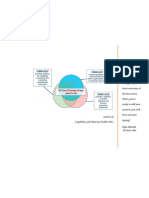
The document outlines Robert James Havighurst's developmental tasks across different life stages, including infancy, childhood, adolescence, early adulthood, middle adulthood, and later maturity. Each stage includes specific tasks that individuals must achieve to foster personal growth and social responsibility. Key tasks include selecting a mate, starting a family, achieving emotional independence, and preparing for an economic career.
Uploaded by
jamesemmanueldupitasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views2 pagesHuman Development
The document outlines Robert James Havighurst's developmental tasks across different life stages, including infancy, childhood, adolescence, early adulthood, middle adulthood, and later maturity. Each stage includes specific tasks that individuals must achieve to foster personal growth and social responsibility. Key tasks include selecting a mate, starting a family, achieving emotional independence, and preparing for an economic career.
Uploaded by
jamesemmanueldupitasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2