0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views13 pages23 Shell Scripting
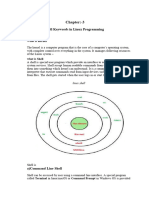
The document provides an overview of Linux architecture, including its components like the shell and kernel, and explains shell scripting, variables, operators, and conditional statements. It also covers the differences between programming and scripting, the use of sha-bang, and how to manage variables in Linux. Additionally, it discusses scheduling tasks using CRON jobs and includes practical examples and assignments related to shell scripting.
Uploaded by
jovisec598Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views13 pages23 Shell Scripting
The document provides an overview of Linux architecture, including its components like the shell and kernel, and explains shell scripting, variables, operators, and conditional statements. It also covers the differences between programming and scripting, the use of sha-bang, and how to manage variables in Linux. Additionally, it discusses scheduling tasks using CRON jobs and includes practical examples and assignments related to shell scripting.
Uploaded by
jovisec598Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 13