0% found this document useful (0 votes)
63 views2 pagesSums Modul Petrel
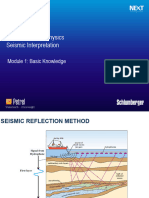
The Petrel Module provides a comprehensive guide for data management, visualization, fault picking, horizon interpretation, cropping volume, mapping, and volume mapping in seismic analysis. Key sessions include project setup, fault identification, hydrocarbon occurrence tracking, and generating reservoir surfaces. The document emphasizes the importance of accurate data handling and visualization techniques for effective interpretation and analysis.
Uploaded by
frewin karubunCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
63 views2 pagesSums Modul Petrel
The Petrel Module provides a comprehensive guide for data management, visualization, fault picking, horizon interpretation, cropping volume, mapping, and volume mapping in seismic analysis. Key sessions include project setup, fault identification, hydrocarbon occurrence tracking, and generating reservoir surfaces. The document emphasizes the importance of accurate data handling and visualization techniques for effective interpretation and analysis.
Uploaded by
frewin karubunCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2