0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views16 pages02 Module 1 Arrays
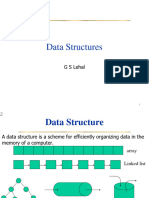
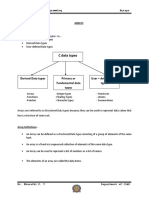
This document serves as a guide to understanding arrays in programming, specifically focusing on their significance, declaration, initialization, and manipulation in C. It covers single and multidimensional arrays, their purposes, and provides quizzes and programming exercises to reinforce learning. Prior knowledge in programming is expected for students engaging with this material.
Uploaded by
Diana RetullaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views16 pages02 Module 1 Arrays
This document serves as a guide to understanding arrays in programming, specifically focusing on their significance, declaration, initialization, and manipulation in C. It covers single and multidimensional arrays, their purposes, and provides quizzes and programming exercises to reinforce learning. Prior knowledge in programming is expected for students engaging with this material.
Uploaded by
Diana RetullaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 16