0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views5 pagesEncoder
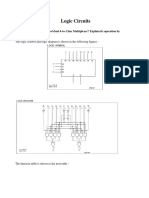
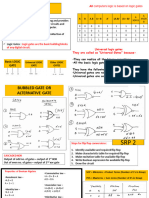
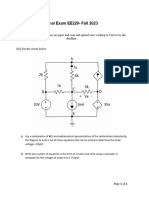
The document discusses the design of a decimal-to-binary encoder and a seven-segment display decoder, explaining their configurations and applications. It also distinguishes between combinational and sequential circuits, detailing the characteristics of flip-flops, including their types and uses. Additionally, it highlights the differences between ZJK and SR flip-flops.
Uploaded by
P NCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views5 pagesEncoder
The document discusses the design of a decimal-to-binary encoder and a seven-segment display decoder, explaining their configurations and applications. It also distinguishes between combinational and sequential circuits, detailing the characteristics of flip-flops, including their types and uses. Additionally, it highlights the differences between ZJK and SR flip-flops.
Uploaded by
P NCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5