Unit 5 : Mysql Revision
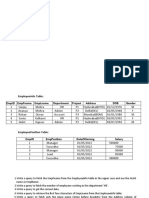
EmployeeInfo Table:
EmpI EmpFna EmpLna Departme Proje Gende
Address DOB
D me me nt ct r
Hyderabad(HY 01/12/19
1 Sanjay Mehra HR P1 M
D) 76
02/05/19
2 Ananya Mishra Admin P2 Delhi(DEL) F
68
Mumbai(BOM 01/01/19
3 Rohan Diwan Account P3 M
) 80
Hyderabad(HY 02/05/19
4 Sonia Kulkarni HR P1 F
D) 92
03/07/19
5 Ankit Kapoor Admin P2 Delhi(DEL) M
94
EmployeePosition Table:
EmpID EmpPosition DateOfJoining Salary
1 Manager 01/05/2022 500000
2 Executive 02/05/2022 75000
3 Manager 01/05/2022 90000
2 Lead 02/05/2022 85000
1 Executive 01/05/2022 300000
Q1. Write a query to fetch the EmpFname from the EmployeeInfo table in upper case
and use the ALIAS name as EmpName.
-> SELECT UPPER(EmpFname) AS EmpName FROM EmployeeInfo;
Q2. Write a query to fetch the number of employees working in the department ‘HR’.
->SELECT COUNT(*) FROM EmployeeInfo WHERE Department = 'HR';
Q3. Write a query to get the current date.
->SELECT GETDATE();
->SELECT SYSTDATE();
Q4. Write a query to retrieve the first four characters of EmpLname from the EmployeeInfo table.
-> SELECT SUBSTRING(EmpLname, 1, 4) FROM EmployeeInfo;
Q5. Write a query to fetch only the place name(string before brackets) from the Address column of
EmployeeInfo table.
Using the MID function in MySQL
-> SELECT MID(Address, 0, LOCATE('(',Address)) FROM EmployeeInfo;
Using SUBSTRING:-
�-> SELECT SUBSTRING(Address, 1, CHARINDEX('(',Address)) FROM EmployeeInfo;
Q6. Write a query to create a new table which consists of data and structure copied from the other
table.
Using the SELECT INTO command:
-> SELECT * INTO NewTable FROM EmployeeInfo WHERE 1 = 0;
Q7. Write q query to find all the employees whose salary is between 50000 to 100000.
-> SELECT * FROM EmployeePosition WHERE Salary BETWEEN '50000' AND '100000';
Q8. Write a query to find the names of employees that begin with ‘S’
-> SELECT * FROM EmployeeInfo WHERE EmpFname LIKE 'S%';
Q9. Write a query to fetch top N records.
By using the TOP command in SQL Server:
->SELECT TOP N * FROM EmployeePosition ORDER BY Salary DESC;
By using the LIMIT command in MySQL:
->SELECT * FROM EmpPosition ORDER BY Salary DESC LIMIT N;
Q10. Write a query to retrieve the EmpFname and EmpLname in a single column as “FullName”.
The first name and the last name must be separated with space.
-> SELECT CONCAT(EmpFname, ' ', EmpLname) AS 'FullName' FROM EmployeeInfo;
Q11. Write a query find number of employees whose DOB is between 02/05/1970 to 31/12/1975 and
are grouped according to gender
-> SELECT COUNT(*), Gender FROM EmployeeInfo WHERE DOB BETWEEN '02/05/1970 ' AND
'31/12/1975' GROUP BY Gender;
Q12. Write a query to fetch all the records from the EmployeeInfo table ordered by EmpLname in
descending order and Department in the ascending order.
-> To order the records in ascending and descnding order, you have to use the ORDER BY statement in
SQL.
-> SELECT * FROM EmployeeInfo ORDER BY EmpFname desc, Department asc;
Q13. Write a query to fetch details of employees whose EmpLname ends with an alphabet ‘A’ and
contains five alphabets.
To fetch details mathcing a certain value, you have to use the LIKE operator in SQL.
SELECT * FROM EmployeeInfo WHERE EmpLname LIKE '____a';
Q14. Write a query to fetch details of all employees excluding the employees with first names,
“Sanjay” and “Sonia”
from the EmployeeInfo table.
SELECT * FROM EmployeeInfo WHERE EmpFname NOT IN ('Sanjay','Sonia');
Q15. Write a query to fetch details of employees with the address as “DELHI(DEL)”.
SELECT * FROM EmployeeInfo WHERE Address LIKE 'DELHI(DEL)%';
Q16. Write a query to fetch all employees who also hold the managerial position.
SELECT E.EmpFname, E.EmpLname, P.EmpPosition
FROM EmployeeInfo E INNER JOIN EmployeePosition P ON
E.EmpID = P.EmpID AND P.EmpPosition IN ('Manager');
Q17. Write a query to fetch the department-wise count of employees sorted by department’s count
in ascending order.
SELECT Department, count(EmpID) AS EmpDeptCount
FROM EmployeeInfo GROUP BY Department
ORDER BY EmpDeptCount ASC;
�Q18. Write a query to calculate the even and odd records from a table.
To retrieve the even records from a table, you have to use the MOD() function as follows:
SELECT EmpID FROM (SELECT rowno, EmpID from EmployeeInfo) WHERE MOD(rowno,2)=0;
Similarly, to retrieve the odd records from a table, you can write a query as follows:
-> SELECT EmpID FROM (SELECT rowno, EmpID from EmployeeInfo) WHERE MOD(rowno,2)=1;
Q19. Write a SQL query to retrieve employee details from EmployeeInfo table who have a date of
joining in the EmployeePosition table.
-> SELECT * FROM EmployeeInfo E
WHERE EXISTS
(SELECT * FROM EmployeePosition P WHERE E.EmpId = P.EmpId);
Q20. Write a query to retrieve two minimum and maximum salaries from the EmployeePosition table.
-> To retrieve two minimum salaries, you can write a query as below:
SELECT DISTINCT Salary FROM EmployeePosition E1
WHERE 2 >= (SELECTCOUNT(DISTINCT Salary)FROM EmployeePosition E2
WHERE E1.Salary >= E2.Salary) ORDER BY E1.Salary DESC;
-> To retrieve two maximum salaries, you can write a query as below:
SELECT DISTINCT Salary FROM EmployeePosition E1
WHERE 2 >= (SELECTCOUNT(DISTINCT Salary) FROM EmployeePosition E2
WHERE E1.Salary <= E2.Salary) ORDER BY E1.Salary DESC;
Q21. Write a query to find the Nth highest salary from the table without using TOP/limit keyword.
-> SELECT Salary
FROM EmployeePosition E1
WHERE N-1 = (
SELECT COUNT( DISTINCT ( E2.Salary ) )
FROM EmployeePosition E2
WHERE E2.Salary > E1.Salary );
Q22. Write a query to retrieve duplicate records from a table.
-> SELECT EmpID, EmpFname, Department COUNT(*)
FROM EmployeeInfo GROUP BY EmpID, EmpFname, Department
HAVING COUNT(*) > 1;
Q23. Write a query to retrieve the list of employees working in the same department.
-> Select DISTINCT E.EmpID, E.EmpFname, E.Department
FROM EmployeeInfo E, Employee E1
WHERE E.Department = E1.Department AND E.EmpID != E1.EmpID;
Q24. Write a query to retrieve the last 3 records from the EmployeeInfo table.
-> SELECT * FROM EmployeeInfo WHERE
EmpID <=3 UNION SELECT * FROM
(SELECT * FROM EmployeeInfo E ORDER BY E.EmpID DESC)
AS E1 WHERE E1.EmpID <=3;
Q25. Write a query to find the third-highest salary from the EmpPosition table.
-> SELECT TOP 1 salary
FROM(
SELECT TOP 3 salary
FROM employee_table
ORDER BY salary DESC) AS emp
ORDER BY salary ASC;
Q26. Write a query to display the first and the last record from the EmployeeInfo table.
To display the first record from the EmployeeInfo table, you can write a query as follows:
-> SELECT * FROM EmployeeInfo WHERE EmpID = (SELECT MIN(EmpID) FROM EmployeeInfo);
�To display the last record from the EmployeeInfo table, you can write a query as follows:
-> SELECT * FROM EmployeeInfo WHERE EmpID = (SELECT MAX(EmpID) FROM EmployeeInfo);
Q27. Write a query to add email validation to your database
-> SELECT Email FROM EmployeeInfo WHERE NOT REGEXP_LIKE(Email, ‘[A-Z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Z0-9.-
]+.[A-Z]{2,4}’, ‘i’);
Q28. Write a query to retrieve Departments who have less than 2 employees working in it.
-> SELECT DEPARTMENT, COUNT(EmpID) as 'EmpNo' FROM EmployeeInfo GROUP BY DEPARTMENT
HAVING COUNT(EmpD) < 2;
Q29. Write a query to retrieve EmpPostion along with total salaries paid for each of them.
->SELECT EmpPosition, SUM(Salary) from EmployeePosition GROUP BY EmpPosition;
Q30. Write a query to fetch 50% records from the EmployeeInfo table.
-> SELECT *
FROM EmployeeInfo WHERE
EmpID <= (SELECT COUNT(EmpID)/2 from EmployeeInfo);