0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views4 pagesCXC IT Syllabus Notes
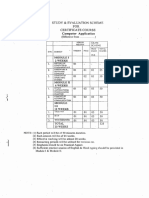
The CXC Information Technology Syllabus covers key areas such as computer fundamentals, networking, social impacts of ICT, word processing, spreadsheets, database management, problem-solving, and program implementation. It emphasizes the importance of understanding hardware and software, networking protocols, ethical issues, and practical skills in programming and data management. Additionally, the syllabus highlights the economic implications of ICT and the need for relevant skills in the evolving job market.
Uploaded by
je8779457Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views4 pagesCXC IT Syllabus Notes
The CXC Information Technology Syllabus covers key areas such as computer fundamentals, networking, social impacts of ICT, word processing, spreadsheets, database management, problem-solving, and program implementation. It emphasizes the importance of understanding hardware and software, networking protocols, ethical issues, and practical skills in programming and data management. Additionally, the syllabus highlights the economic implications of ICT and the need for relevant skills in the evolving job market.
Uploaded by
je8779457Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4