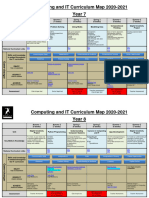
Key Stage 3 Curriculum aims Curriculum content Curriculum Delivery
Computing/ICT
Our academies will build on the curriculum given • E-Safety– The study of a cyberbullying, online safety, safer Each topic is delivered through lesson time
Year 7 by partner primary schools to help students build use of IT systems. with additional opportunities to expand
confidence when using and understanding • Programming – An introduction into programming students knowledge outside of class time
computing systems. techniques, flowcharts and concepts. Computational via online learning.
thinking.
We aim to make students effective users of IT
• Modelling and Finance– Spreadsheet modelling and skills.
systems and be confident with navigation through Typically, each unit will comprise of around
• Hardware and software– The components of a computer
operating systems, office applications and the and how they function. Encryption. 7 weeks of teaching and will culminate in
wider global internet. • Creative Media & Web design– Design and web page either a short summative assessment or be
We aim to ensure students understand the manipulation. Website production and creation. assessed with a more holistic project based
dangers and implications of using different viewpoint with students producing products
technologies. over a longer period of time.
The curriculum in Year 8 will deepen students’ • Python Programming– basic and advanced concepts in Typically, each unit will comprise of around
Year 8 understanding of how computing has evolved and programming. 7 weeks of teaching and will culminate in a
strengthen knowledge of concepts from Year 7. • Databases or Imedia*–Database structures and practical summative assessment or
Teaching will begin to integrate more construction OR graphic manipulation and animation. presentation of work completed over a
(*dependant of school)
sophisticated practical skills for creation of short time.
• Online safety /Cyber security– Sexting, Mobile devices,
products and deeper the analysis and research Students will be assessed on their team
cybersecurity and backups.
skills needed in projects. A strong emphasis will be • Website – Advanced concepts, embedding multimedia work and project approaches as well as
placed upon exploring computing for pleasure and elements and forms. Careers research embedded within verbal feedback given on their careers
personal development in this field. topic. research.
Careers and pathways for the future will be • Office skills – The practical use of Word processors, Students are encouraged whenever possible
discussed with students as well as exploring team presentation software, spreadsheets and email. to communicate using the median of IT
based project work. • Game Making – Computer game design and creation and systems.
project work concepts.
�Key Stage 4 Curriculum aims Curriculum content Curriculum Delivery
Computer Science OCR Computer Science (9-1)
The GCSE in Computer Science is engaging and practical, • Unit 1 Computer Systems – This unit covers the Each Theory chapter is delivered
Year 9 encouraging creativity and problem solving. It encourages following topics to be studied in this order: through lesson time with additional
students to develop their understanding and application of 1.1 System Architecture / processors opportunities to expand students
the core concepts in computer science. Students also 1.2 Memory knowledge outside of class time.
1.3 Storage
analyse problems in computational terms and devise
1.4 Wired and Wireless Networks
creative solutions by designing, writing, testing and Typically, each chapter will be assessed
1.5 Network Topologies and protocols
evaluating programs. 1.6 System Security formatively during lessons and then a
It aims to help students understand the components that 1.7 Ethical, legal and cultural concerns short summative assessment at the
make up digital systems, and how they communicate • Practical Python Programming sills – based on end of each chapter. A past paper will
with one another and with other systems. input/output and project work. be used at the end of studying Unit 1 to
The curriculum aims to install a love for learning in students. determine student knowledge base.
The curriculum builds in Year 10 to encourage learners to • Unit 2 Computational thinking, algorithms and Typically, each chapter will be assessed
Year 10 become responsible for their own learning, confident in programming. This unit covers the following topics: formatively during lessons and then a
discussing ideas, innovative and engaged. 2.1Algorithms short summative assessment at the
Student will understand and apply the fundamental 2.2 Programming Techniques end of each chapter. A past paper will
2.3 Producing robust programs
principles and concepts of Computer Science, be used at the end of studying Unit 2 to
2.4 Computational Logic
including abstraction, decomposition, logic, determine student knowledge base.
2.5 Translators and facilities of language
algorithms, and data representation. 2.6 Data Representation Practical tasks will be assessed visually
• Practical skills in python ready to complete the Unit and with the aid of online tools.
3 practical task.
Build on and reinforce the previous knowledge gained, • Unit 3 – Practical task requiring students to GCSE EXAM in Unit 1 Computer
Year 11 whilst understand the impacts of digital technology programme a product to meet an exam board set systems (50% of final grade)
to the individual and to wider society. Keeping in mind task. GCSE EXAM in Unit 2 Computational
recent developments in technology. • Revision of Unit 1 – all chapters thinking, algorithms and programming
• Revision for Unit 2 – all chapters
(50% of the final grade)
�Key Stage 4 Curriculum aims Curriculum content Curriculum Delivery
iMedia
In Year 9 the course will aim to develop • Autumn – Photoshop/Graphics Soft Skills and skills development Work will be delivered and assessed through MS
Year 9 soft ICT skills, building products and • Spring – Continue to work on soft skills as well as introducing the R081 Teams or electronic submission of assignments.
training students to meet the potential contents to share knowledge of pre production skills and methodologies.
scenarios of the business world. The aim • Summer – Continue the previous terms work, begin to bring in other soft The Soft Skills will be skills based exercises with
is to develop students ability to evaluate skills for other units, eg web design, multimedia reviews, video, etc. assessments base don local context and interests.
and reflect on their work, whilst learning • Throughout years 9 & 10 other opportunities will be taken as they arise,
to manage small system lifecycles and such as https://idea.org.uk in order to extend the boundaries of learning. More summative assessments will appear in the
project based approaches. (Research – Spring, with the focus on practice assessments and
Design – Build – Evaluate.) outcomes.
To fully understand and develop Learner will cover topics for Units R081 and R082 from the OCR iMedia Each unit has an formal assessment at the end,
Year 10 knowledge of preproduction's Cambridge Nationals Level 1 / 2 course. where staff have guidance and rules from the
procedures for any digital product. This includes: exam board OCR and JCQ.
Students will aim to have a working -Understand the purpose and content of pre-production. Autumn – Work on R081 material and begin to
knowledge of how to produce high -Planning a pre-production and producing documentation. work on R082 practice work
quality digital products and what factors -Reviewing preproduction materials Spring – R082 material and R081 pre production
to consider when undertaking project -Understanding the purpose and properties of digital graphics. material. Aim for submission of R082 in the
work. -Planning the creation of a digital graphic. summer window – Mid May
-Creating a digital graphic. Summer – EXAM + Begin soft skills in 3th and 4th
-Reviewing digital graphics units selected by centres and completed in year 11
Using the foundation knowledge gained In Year 11 student will complete and finish the remaining two units of the OCR Autumn – Aim to complete 3rd unit for January
Year 11 in the previous two years, students are to iMedia course. entry with exam board.
broaden their skill set and working These units will be selected by each school based on the students they are Spring – Begin work on final coursework unit for
knowledge of specific digital products teaching that year, students interests, available technology, software available submission
and be able to give students the maturity within each centre and staff expertise. Summer – resubmissions if required.
to evaluate and review multiple digital Units might include; Website production, 3D graphics, digital animation,
projects. storyboarding, sound sequencing, video, photography, game design and
development.