0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views19 pagesLecture 4 - Input Output
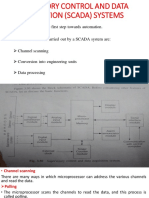
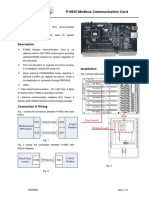
The document provides an introduction to embedded systems, focusing on input and output mechanisms, including sampling rates and event inputs. It discusses the importance of input conditioning, filtering, and handling electrical issues related to I/O operations. Additionally, it addresses challenges such as pin shortages and methods to manage them through time-multiplexing and encoding techniques.
Uploaded by
tekeba lakeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views19 pagesLecture 4 - Input Output
The document provides an introduction to embedded systems, focusing on input and output mechanisms, including sampling rates and event inputs. It discusses the importance of input conditioning, filtering, and handling electrical issues related to I/O operations. Additionally, it addresses challenges such as pin shortages and methods to manage them through time-multiplexing and encoding techniques.
Uploaded by
tekeba lakeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 19