0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views8 pagesBio Paper
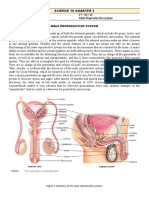
The document outlines various birth control methods, including barrier methods, hormonal methods, intrauterine devices, sterilization, natural methods, and emergency contraception. It details the mechanisms, effectiveness, and side effects of each method, emphasizing the importance of medical supervision for certain procedures. Additionally, it discusses the benefits and risks associated with birth control pills, highlighting the need for proper usage and consultation with healthcare providers.
Uploaded by
kareemqahoush72Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views8 pagesBio Paper
The document outlines various birth control methods, including barrier methods, hormonal methods, intrauterine devices, sterilization, natural methods, and emergency contraception. It details the mechanisms, effectiveness, and side effects of each method, emphasizing the importance of medical supervision for certain procedures. Additionally, it discusses the benefits and risks associated with birth control pills, highlighting the need for proper usage and consultation with healthcare providers.
Uploaded by
kareemqahoush72Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8