0% found this document useful (0 votes)
439 views2 pagesConstruction and Installation Methodology
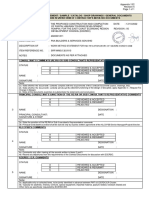
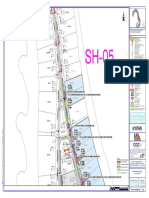
The document outlines the construction and installation methodology for an underground sewer line, detailing phases from pre-construction site surveys to final commissioning and handover. Key steps include excavation, pipe installation, backfilling, testing for leaks, and surface restoration. The process emphasizes safety, proper alignment, and thorough documentation for client handover.
Uploaded by
srqaengrgccCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
439 views2 pagesConstruction and Installation Methodology
The document outlines the construction and installation methodology for an underground sewer line, detailing phases from pre-construction site surveys to final commissioning and handover. Key steps include excavation, pipe installation, backfilling, testing for leaks, and surface restoration. The process emphasizes safety, proper alignment, and thorough documentation for client handover.
Uploaded by
srqaengrgccCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2