0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views29 pagesCRM Module-5
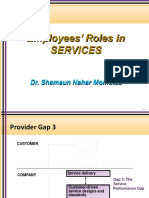
The document discusses the evolution of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and its significance in various industries, emphasizing the role of technology in enhancing customer interactions. It highlights the importance of employee satisfaction in fostering customer loyalty and outlines strategies for building strong employee-customer relationships. Additionally, it addresses service failures and the concept of service recovery, noting that effectively resolving issues can lead to higher customer satisfaction than if no problems had occurred at all.
Uploaded by
Ashita SavsaniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views29 pagesCRM Module-5
The document discusses the evolution of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and its significance in various industries, emphasizing the role of technology in enhancing customer interactions. It highlights the importance of employee satisfaction in fostering customer loyalty and outlines strategies for building strong employee-customer relationships. Additionally, it addresses service failures and the concept of service recovery, noting that effectively resolving issues can lead to higher customer satisfaction than if no problems had occurred at all.
Uploaded by
Ashita SavsaniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 29